Metal extrusion is a versatile manufacturing process that forces metal through a die to create parts with consistent cross-sectional profiles. This transformative technique allows manufacturers to produce complex shapes with excellent mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy. At MAIKONG, we’ve mastered the art and science of metal extrusion to deliver superior quality components for industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to construction and electronics.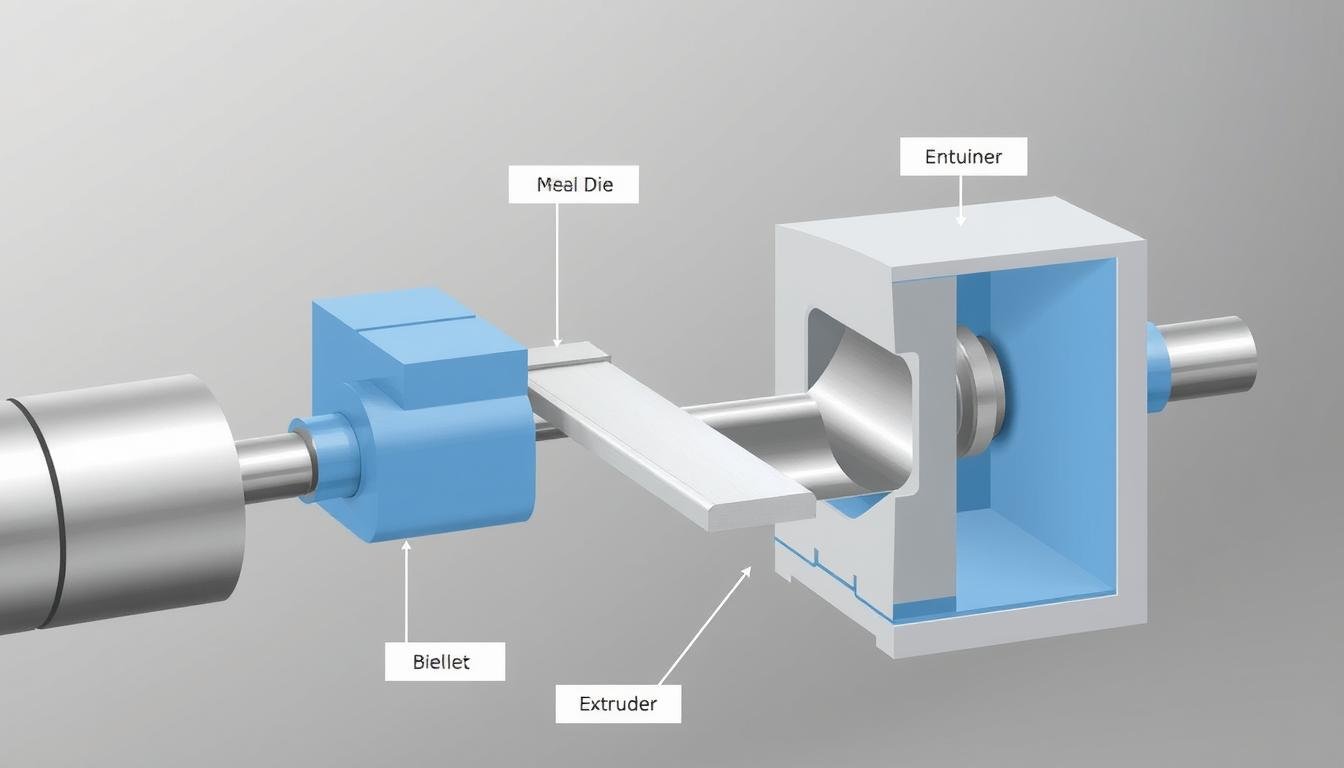
Types of Metal Extrusion Processes
The metal extrusion industry employs several different methods, each with unique advantages for specific applications. Understanding these variations helps in selecting the optimal process for your manufacturing needs.
Hot Extrusion
In hot extrusion, the feed metal is heated above its recrystallization temperature, softening it to flow more easily through the die opening. This method prevents work hardening and allows for greater deformation of the material.
Advantages:
- Allows for greater deformation and higher extrusion ratios
- Reduces required force and power consumption
- Eliminates work hardening during the process
Disadvantages:
- Higher equipment costs for heating and maintenance
- Potential for surface oxidation requiring removal
- Only profitable for larger production runs
Cold Extrusion
Cold extrusion is performed at room temperature or with only slight heating. The material maintains its original properties throughout the process, resulting in different mechanical characteristics in the final product.
Advantages:
- Superior surface finish with no oxidation
- Better dimensional accuracy and tighter tolerances
- Improved mechanical properties through work hardening
Disadvantages:
- Requires more power due to higher material resistance
- Limited deformation capability compared to hot extrusion
- Lower extrusion speeds and production rates
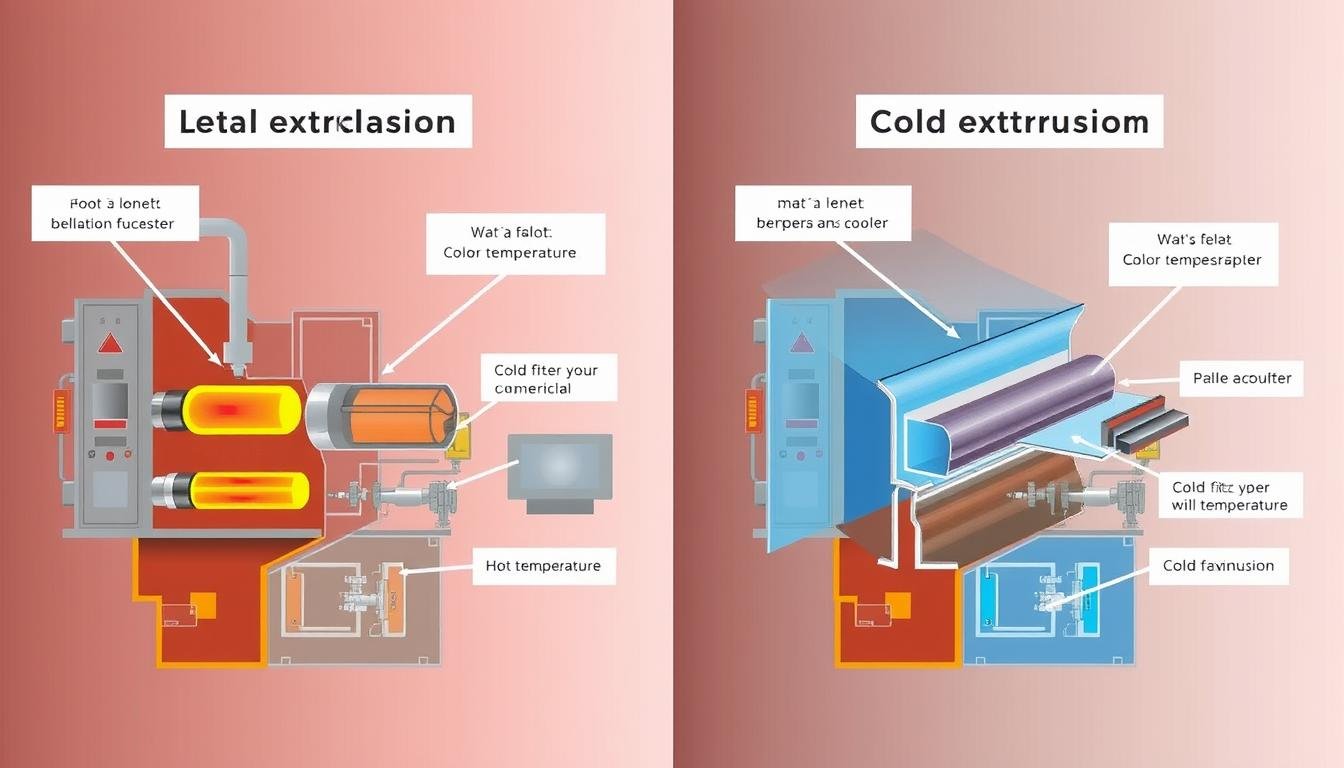
Comparison of hot and cold extrusion processes and their effects on the metal structure
Warm Extrusion
Warm extrusion operates at temperatures between room temperature and the material’s recrystallization point. This middle-ground approach offers a balance of benefits from both hot and cold methods, with temperatures typically ranging from 424°C to 975°C depending on the material.
Friction Extrusion
This innovative process uses the heat generated from friction between the die and feed metal to reach optimal extrusion temperature. No preheating is required, as the process utilizes internal energy from friction. A significant advantage is the ability to use recyclable metal scraps, blocks, machining chips, and powder directly as feed material without pretreatment.
Extrusion Equipment and Methods
The equipment used in metal extrusion varies based on the specific technique employed. Each method offers distinct advantages for different production requirements.
Direct Extrusion
In direct (forward) extrusion, a stationary die is used while the ram creates pressure on the metal. The extruded part emerges in the same direction as the ram motion. This is the most common extrusion method due to its simplicity and versatility.
Key Characteristics:
- Simple tooling requirements
- Compatible with both hot and cold extrusion
- No modification needed to the billet
- Higher friction forces requiring greater extrusion pressure
Indirect Extrusion
Indirect (backward) extrusion features a die opening on the ram itself. As the punch compresses the metal, it flows through the die in the opposite direction of ram movement, reducing friction between the billet and container.
Key Characteristics:
- Lower power consumption due to reduced friction
- More consistent extrusion pressure throughout the process
- Limited by the hollow ram’s load capacity
- Challenges in supporting the extrudate as it emerges
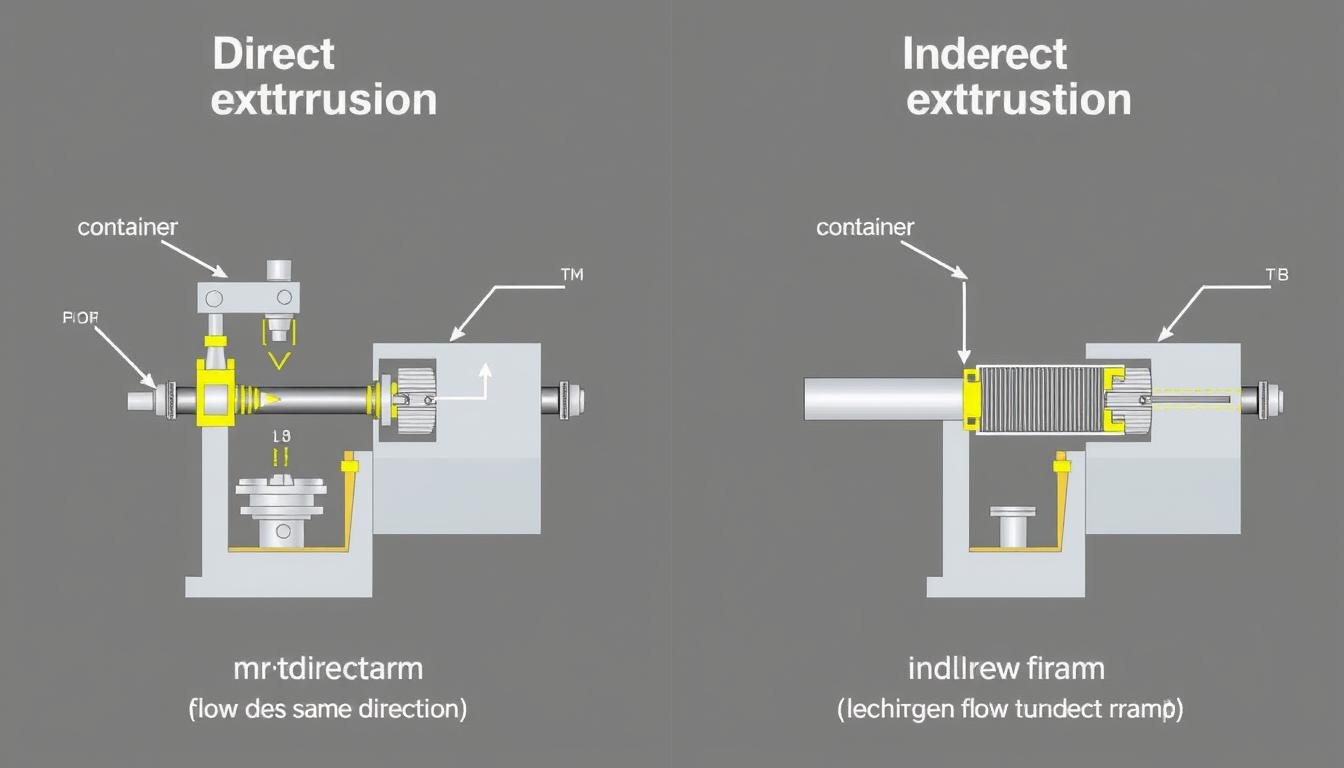
Comparison of direct and indirect extrusion equipment configurations
Hydrostatic Extrusion
Hydrostatic extrusion uses fluid pressure rather than direct ram contact to pressurize the billet. The billet is surrounded by fluid on all sides except where it contacts the die, eliminating friction between the billet and container and reducing the required force.
Advantages:
- Lower extrusion forces required
- Even material flow resulting in consistent properties
- Lower billet temperature during processing
- No billet residue left in the container
Impact Extrusion
Impact extrusion involves bringing a punch into contact with the billet at high speed. The resulting pressure forces the material out through the clearance between the punch and die, creating the desired shape. This method is primarily used for cold extrusion of softer metals like aluminum, copper, and lead.
Need Expert Metal Extrusion Services?
MAIKONG provides comprehensive metal extrusion solutions with industry-leading quality control and competitive pricing. Contact our engineering team today!
Contact via WhatsApp
Email Us
Materials for Metal Extrusion
While metal extrusion can be applied to various materials, certain metals and alloys are particularly well-suited to this manufacturing process. The choice of material significantly impacts the extrusion parameters, equipment requirements, and final product properties.
| Metal/Alloy |
Extrusion Temperature |
Key Properties |
Common Applications |
| Aluminum (6061) |
800-930°F |
High strength, good corrosion resistance, excellent fatigue resistance |
Transportation components, structural applications |
| Aluminum (6063) |
800-925°F |
Good surface finish, corrosion resistance, thin-wall capability |
Architectural components, heat sinks, decorative trim |
| Copper |
1300-1800°F |
Excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, ductility |
Electrical components, heat exchangers, plumbing |
| Brass |
1300-1650°F |
Good corrosion resistance, machinability, aesthetic appeal |
Decorative components, plumbing fixtures, musical instruments |
| Steel |
2000-2300°F |
High strength, durability, wear resistance |
Structural components, automotive parts, tools |
| Magnesium |
650-850°F |
Extremely lightweight, good strength-to-weight ratio |
Aerospace components, lightweight structures |
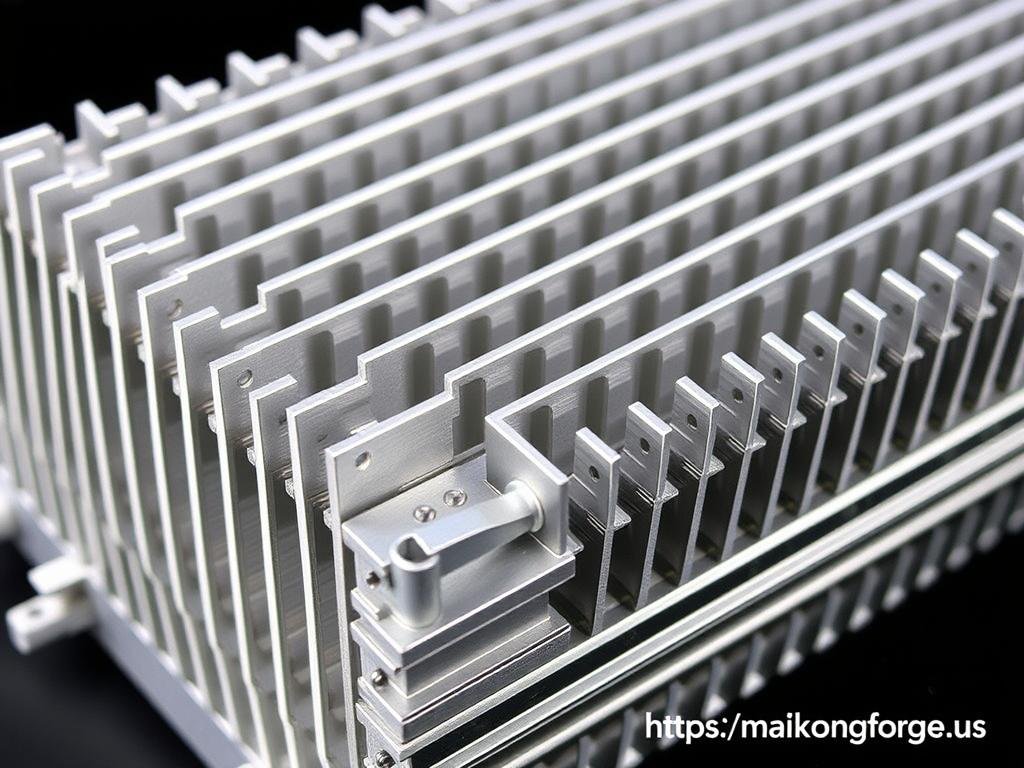
Aluminum Extrusion
Aluminum is the most commonly extruded metal, accounting for approximately 80% of all extruded metal products. Its popularity stems from its excellent formability, lightweight properties, and versatility across industries.

Various aluminum extrusion profiles showcasing the versatility of the process
At MAIKONG, we specialize in aluminum extrusion with a focus on the 6000 series alloys (6061 and 6063), which offer an optimal balance of strength, formability, and corrosion resistance. These alloys can be heat-treated to achieve specific mechanical properties tailored to your application requirements.
Steel Extrusion
Steel extrusion requires significantly higher temperatures and forces than aluminum but produces components with exceptional strength and durability. Our advanced equipment allows us to extrude various steel alloys for applications requiring superior mechanical properties.
Copper and Brass Extrusion
Copper and brass extrusions are valued for their excellent electrical conductivity, thermal properties, and corrosion resistance. These materials are ideal for electrical components, heat exchangers, and decorative applications where their distinctive appearance is desirable.
Common Defects in Metal Extrusion
Despite the many advantages of metal extrusion, certain defects can occur during the process. Understanding these potential issues helps in implementing preventive measures and quality control procedures.
Surface Cracking
Surface cracks form when excessive stresses develop on the material surface, often due to high friction during extrusion. These defects compromise both the aesthetic quality and structural integrity of the extruded product.
Prevention:
- Optimize lubrication
- Control extrusion speed
- Maintain proper temperature
Internal Cracking
Internal cracks develop in the center of the extruded product, typically caused by low friction and low extrusion ratios in the deformation zone. These hidden defects can significantly weaken the structural integrity of the component.
Prevention:
- Increase friction at tool-billet interface
- Adjust extrusion ratio
- Control material flow
Piping
Piping refers to funnel-shaped voids that form in the end product, usually caused by impurities or oxides in the stock material. These defects create weak points and potential failure sites in the extruded component.
Prevention:
- Use high-quality raw materials
- Implement proper cleaning procedures
- Optimize billet preparation
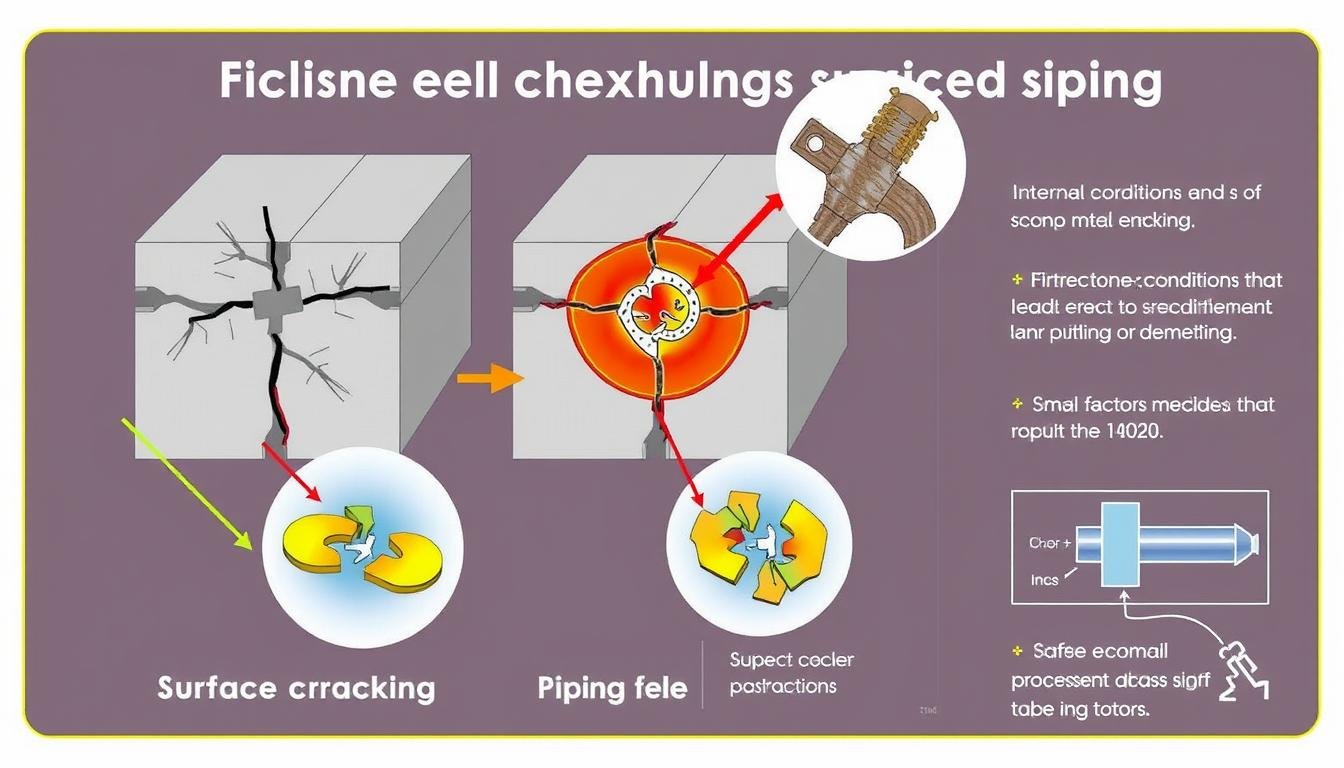
Visual guide to common extrusion defects: surface cracking, internal cracking, and piping
At MAIKONG, our rigorous quality control procedures and advanced equipment minimize the risk of these defects. We implement comprehensive inspection protocols throughout the production process to ensure that every component meets our stringent quality standards.
Design Considerations for Metal Extrusion
Successful metal extrusion requires careful consideration of design parameters to ensure manufacturability, quality, and cost-effectiveness. Following these design guidelines will help optimize your extrusion projects:
Wall Thickness
Maintaining appropriate and uniform wall thickness is crucial for successful extrusion. Thin walls may cause distortion, while excessively thick sections waste material and increase weight.
The minimum wall thickness for aluminum extrusions typically ranges from 1mm for small profiles to 3mm for larger ones. For steel extrusions, minimum wall thickness generally starts at 3mm.
Corner Radii
Sharp corners should be avoided in extrusion designs, as they can cause die failure and material flow issues. Implementing appropriate corner radii improves material flow and extends die life.
| Wall Thickness (mm) |
Recommended Corner Radius (mm) |
| 0-2 |
0.5-1.0 |
| 2-4 |
1.0-1.6 |
| 4-6 |
1.6-2.5 |
| 6-10 |
2.5-4.0 |
Symmetry and Balance
Symmetrical profiles extrude more uniformly and with better dimensional accuracy. When asymmetrical designs are necessary, consider balancing the cross-section to promote even material flow and minimize distortion.
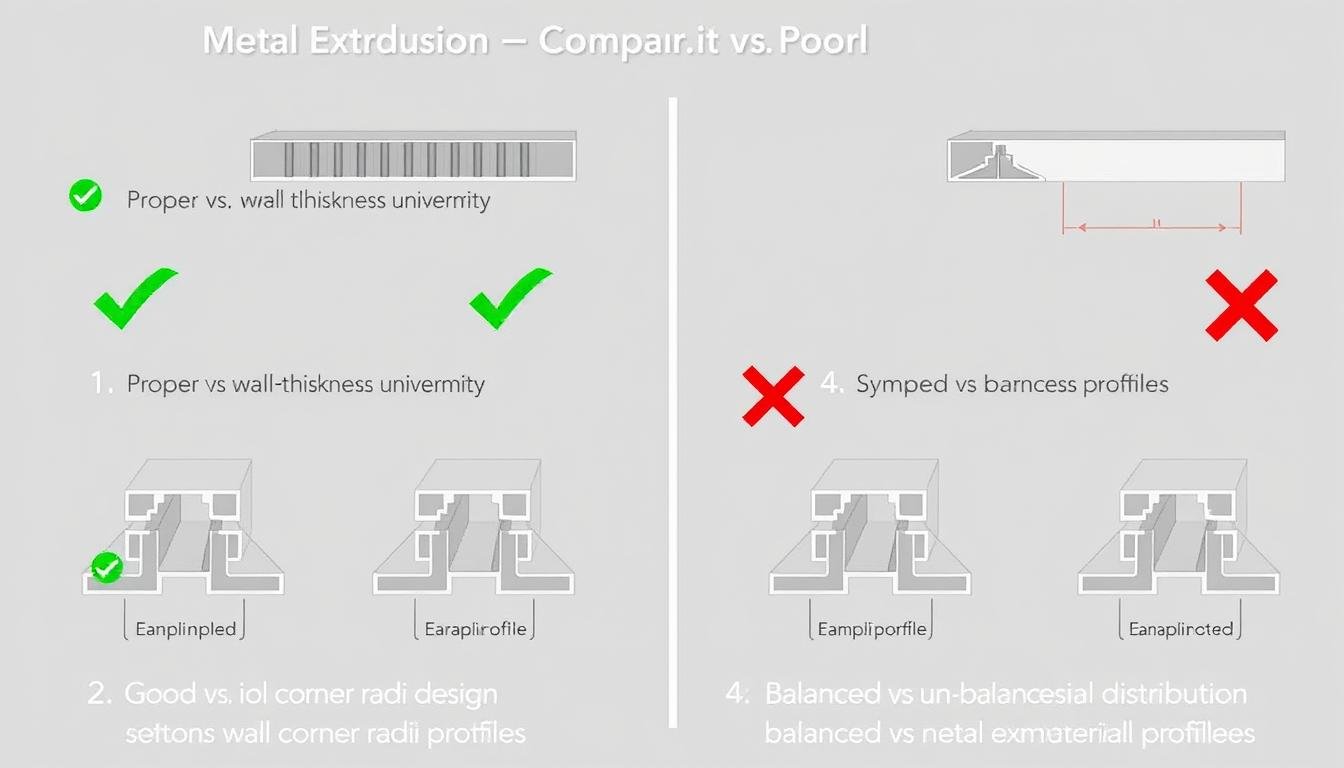
Good vs. poor design practices for metal extrusion profiles
Tolerances
Realistic tolerances should be specified based on the material, profile complexity, and equipment capabilities. Tighter tolerances increase production costs and may require secondary operations.
Design Tip: Metal dimensions (across solid sections) can be held to tighter tolerances than space dimensions (across open gaps). When critical dimensions are required, design your part to utilize metal dimensions for these features.
Design Assistance for Your Metal Extrusion Projects
MAIKONG’s engineering team can help optimize your designs for manufacturability, quality, and cost-effectiveness. Contact us for a design review or consultation.
Request Design Consultation
Applications of Metal Extrusion
Metal extrusion products are ubiquitous in modern industry and everyday life. The versatility of the process allows for applications across numerous sectors:
Construction and Architecture
- Window and door frames
- Structural framing systems
- Curtain wall components
- Railings and handrails
- Decorative trim and moldings
Transportation
- Automotive structural components
- Heat sinks for electric vehicles
- Aircraft structural members
- Railway car components
- Marine applications
Electronics and Electrical
- Heat sinks for electronic components
- LED lighting housings
- Electrical enclosures
- Cable management systems
- Solar panel framing
Industrial Equipment
- Conveyor systems
- Machine guards and frames
- Pneumatic and hydraulic cylinders
- Robotic components
- Factory automation equipment
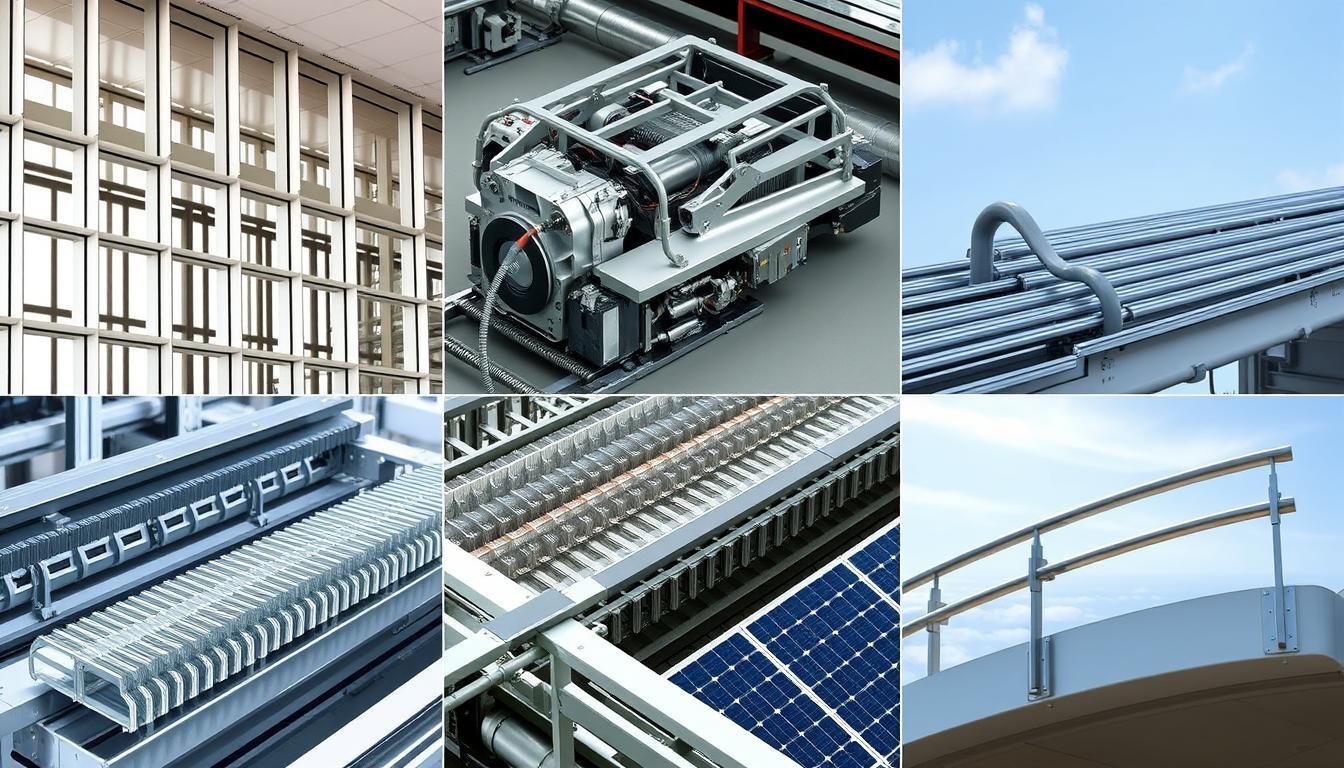

Diverse applications of metal extrusion across multiple industries
Consumer Products
Beyond industrial applications, extruded metal components are found in numerous consumer products, including:
- Furniture frames and components
- Sporting equipment (bicycle frames, tennis rackets)
- Appliance housings and components
- Ladders and scaffolding
- Picture frames and display systems
At MAIKONG, we’ve supplied extruded components for applications across all these industries and more. Our expertise in metal extrusion allows us to deliver high-quality, cost-effective solutions for even the most demanding applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Metal Extrusion
Like any manufacturing process, metal extrusion offers specific benefits and limitations that should be considered when selecting a production method for your components.
Advantages
- Complex Cross-Sections: Ability to create intricate profiles that would be difficult or impossible with other processes
- Material Efficiency: Minimal waste compared to machining or other subtractive processes
- Excellent Surface Finish: Smooth surfaces that often require minimal post-processing
- Enhanced Mechanical Properties: Improved grain structure and strength in the direction of extrusion
- Consistent Dimensions: Uniform cross-section throughout the length of the product
- Cost-Effective for High Volumes: Lower per-unit costs for large production runs
- Wide Material Range: Suitable for numerous metals and alloys
Disadvantages
- Initial Tooling Cost: Die design and fabrication represent a significant upfront investment
- Design Limitations: Cross-section must remain constant throughout the length
- Size Constraints: Limited by press capacity and die size
- Lead Times: Die production and setup can extend initial production timelines
- Post-Processing Requirements: Secondary operations often needed for features like holes, threads, or non-uniform sections
- Minimum Order Quantities: May not be economical for very small production runs
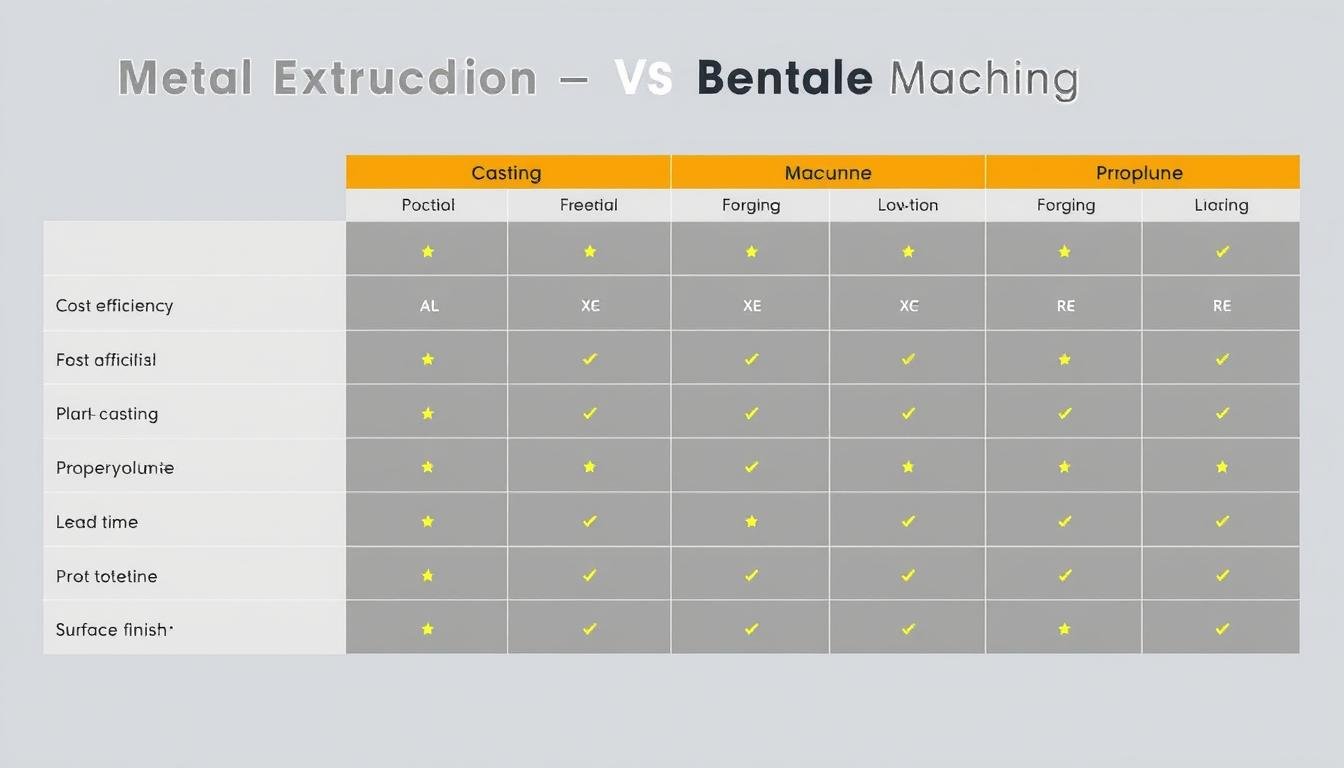
Comparative analysis of metal extrusion versus alternative manufacturing methods
When evaluating whether metal extrusion is the right process for your application, consider factors such as production volume, design complexity, material requirements, and budget constraints. MAIKONG’s engineering team can help you determine if extrusion is the optimal manufacturing method for your specific needs.
MAIKONG’s Metal Extrusion Capabilities
At MAIKONG, we offer comprehensive metal extrusion services backed by decades of experience and state-of-the-art equipment. Our facilities in GD, SZ are equipped with over 60 CNC machines providing more than 100 tons of metal processing capacity per month.
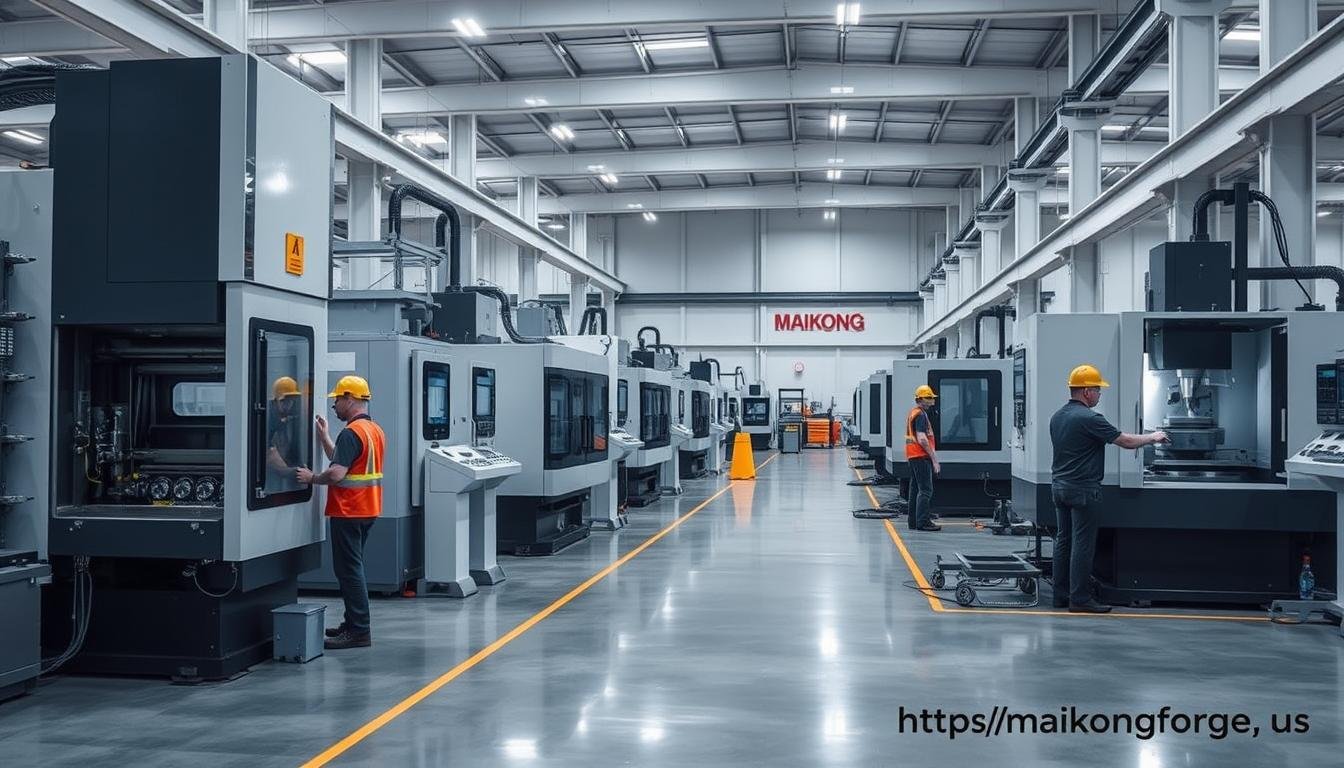

MAIKONG’s advanced metal extrusion facility in GD, SZ
Our Equipment
Our production facility features advanced extrusion presses ranging from 800 to 3500 tons, capable of producing profiles with circumscribing circles up to 300mm. This diverse equipment lineup allows us to handle projects of virtually any size and complexity.
Materials We Work With
- Aluminum alloys (1000, 2000, 5000, 6000, and 7000 series)
- Copper and copper alloys
- Brass and bronze
- Carbon and alloy steels
- Stainless steel
- Specialty alloys
Value-Added Services
Beyond basic extrusion, we offer a comprehensive suite of secondary operations and value-added services:
Precision Machining
- CNC milling and turning
- Swiss-type machining
- Multi-axis machining
- Surface grinding
- Laser engraving
Surface Treatments
- Anodizing (Type I, II, and III)
- Powder coating
- Wet painting
- Plating
- Chemical film
Quality Assurance
- Dimensional inspection
- Material testing
- Non-destructive testing
- First article inspection
- Comprehensive documentation
Partner with MAIKONG for Your Metal Extrusion Needs
Experience the MAIKONG difference with our comprehensive metal extrusion services, technical expertise, and commitment to quality.
Get a Quick Quote
Or contact us directly:
+86 13510907401
Email Us
Quality Control in Metal Extrusion
At MAIKONG, quality is at the core of everything we do. Our comprehensive quality control system ensures that every metal extrusion component meets or exceeds customer specifications and industry standards.
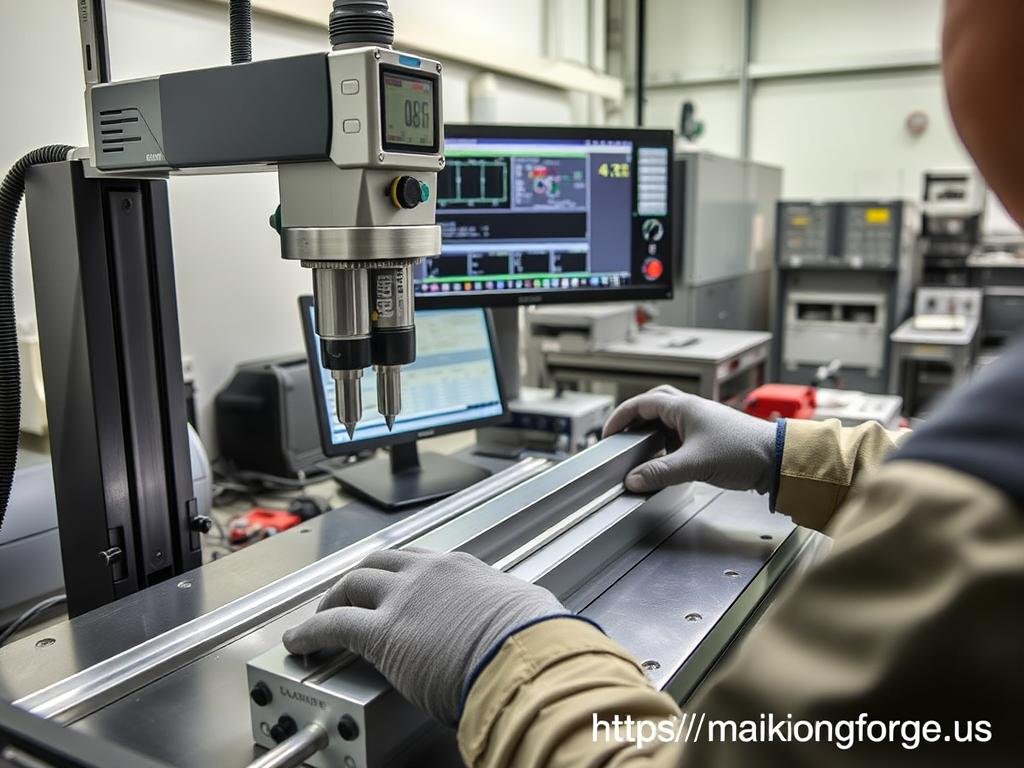

Precision quality inspection of extruded components at MAIKONG’s facility
Our Quality Control Process
Quality control begins with the raw materials and continues throughout the entire production process:
- Material Verification: We test all incoming materials to ensure they meet specified chemical composition and mechanical properties.
- Die Inspection: Before production, all dies undergo rigorous inspection to verify dimensions and surface quality.
- In-Process Monitoring: During extrusion, we continuously monitor critical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and speed.
- Dimensional Inspection: Extruded profiles are regularly checked against specifications using precision measuring equipment.
- Surface Quality Assessment: We inspect for surface defects, ensuring aesthetic and functional requirements are met.
- Mechanical Testing: When required, we perform tensile, hardness, and other mechanical tests to verify material properties.
- Final Inspection: Before shipping, all products undergo a comprehensive final inspection.
Quality Certifications
MAIKONG maintains rigorous quality management systems certified to international standards:
- ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management System
- IATF 16949 Automotive Quality Management System
- Compliance with industry-specific standards and regulations
Our commitment to quality ensures that you receive consistent, reliable products that perform as expected in your applications. We provide comprehensive documentation, including material certifications, inspection reports, and test results, to support your quality requirements.
Metal Extrusion Case Studies
The following case studies highlight MAIKONG’s expertise in metal extrusion and our ability to solve complex manufacturing challenges:
Automotive Heat Sink Solution
Challenge: A leading automotive manufacturer needed a complex heat sink for electric vehicle battery cooling with tight tolerances and high thermal efficiency.
Solution: MAIKONG developed a custom aluminum extrusion profile with optimized fin design and integrated mounting features, reducing assembly steps and improving thermal performance.
Result: The solution reduced weight by 22%, improved cooling efficiency by 15%, and eliminated four assembly operations, saving the client significant production costs.
Architectural Framing System
Challenge: An architectural firm required a custom framing system for a high-rise building with specific aesthetic requirements and structural performance needs.
Solution: We designed and produced a series of interlocking aluminum extrusions with integrated weatherproofing features and hidden fastening systems.
Result: The system met all structural requirements while achieving the desired aesthetic, reducing installation time by 30% compared to conventional systems.
These examples demonstrate our ability to leverage metal extrusion technology to solve complex design and manufacturing challenges across diverse industries. Our engineering team works closely with clients to understand their specific requirements and develop optimized solutions.
Conclusion
Metal extrusion is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process that enables the production of complex profiles with excellent mechanical properties and dimensional consistency. From architectural components to automotive parts, electronics housings to industrial equipment, extruded metal products play a crucial role in countless applications across diverse industries.
At MAIKONG, we combine advanced equipment, technical expertise, and rigorous quality control to deliver superior metal extrusion solutions tailored to your specific requirements. Whether you need standard profiles or custom designs, small production runs or high-volume manufacturing, our team is ready to help you achieve your goals.
Contact us today to discuss your metal extrusion project and discover how MAIKONG can help bring your designs to life with precision, quality, and cost-effectiveness.

The MAIKONG team: Your partners in metal extrusion excellence














