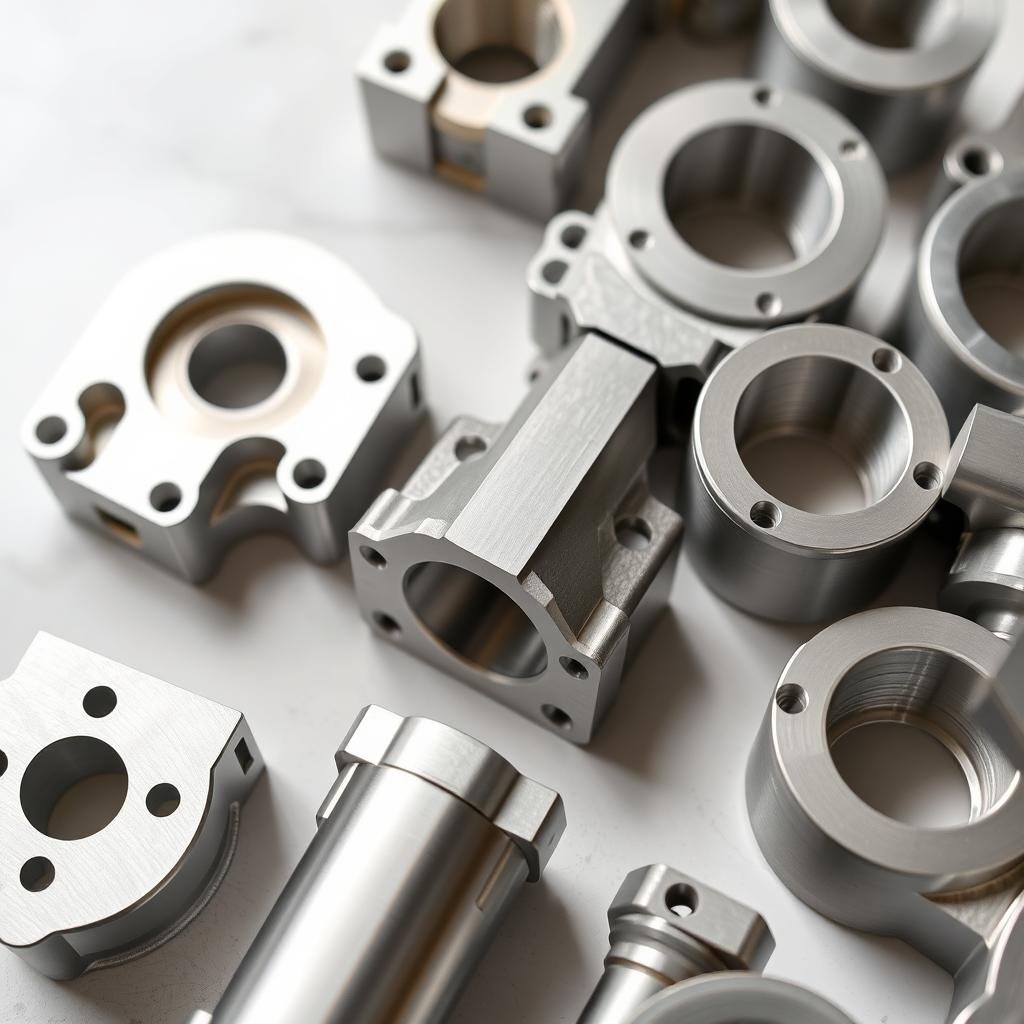
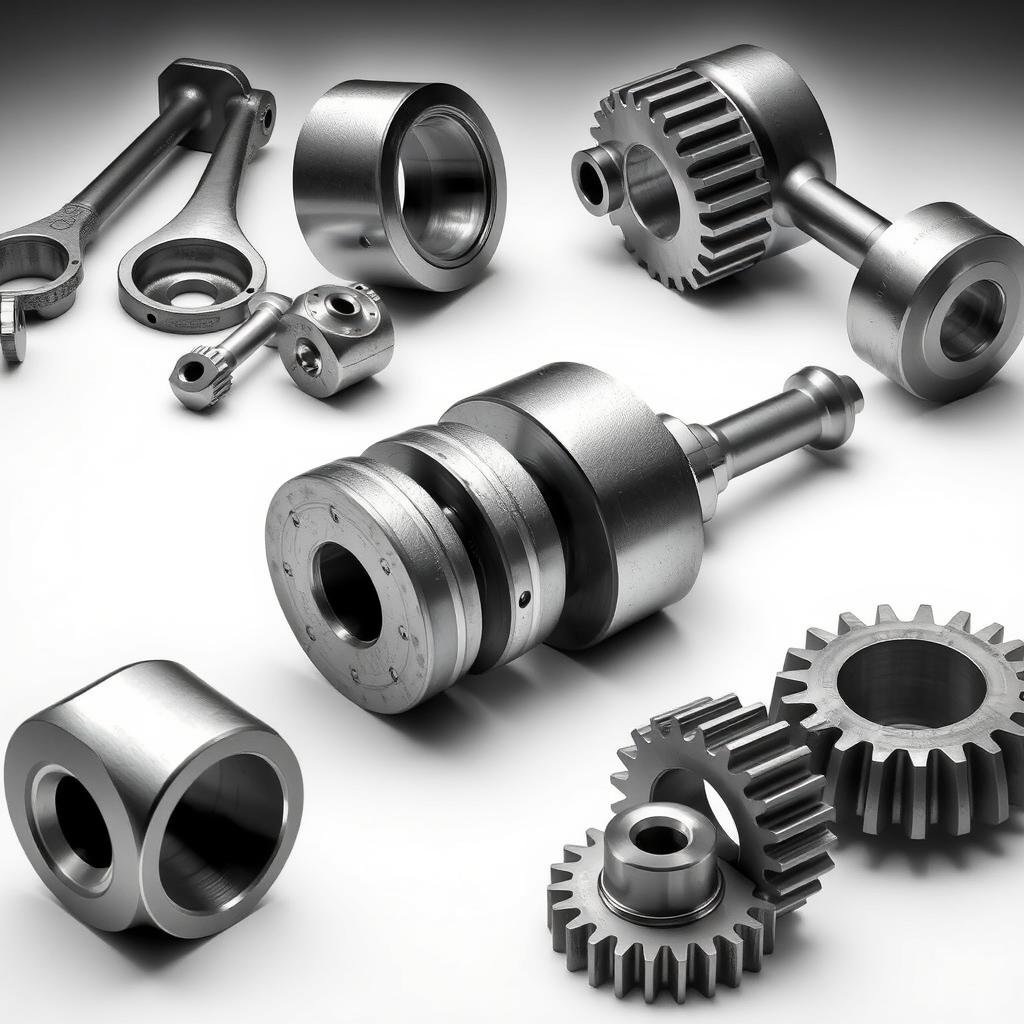
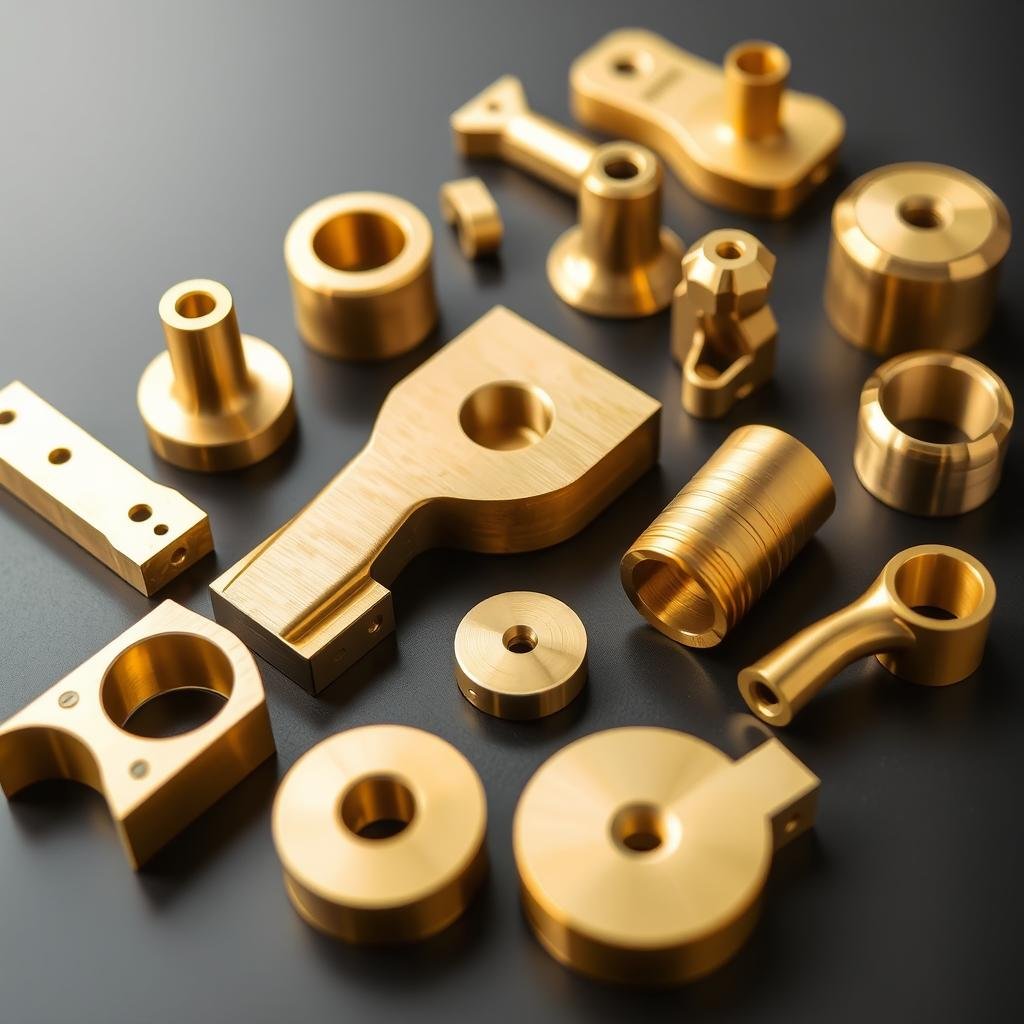
Metal forging stands as one of humanity’s oldest manufacturing techniques, transforming raw metals into tools, weapons, and components that have built civilizations. The evolution of Metal Forging Procedures from ancient blacksmiths to modern precision manufacturing represents a fascinating journey of innovation and technical advancement. Today, these procedures continue to be vital in producing high-strength, durable components for critical applications across industries. This article explores the rich history of metal forging in the United States and how companies like MAIKONG are advancing these time-tested techniques with modern precision and efficiency.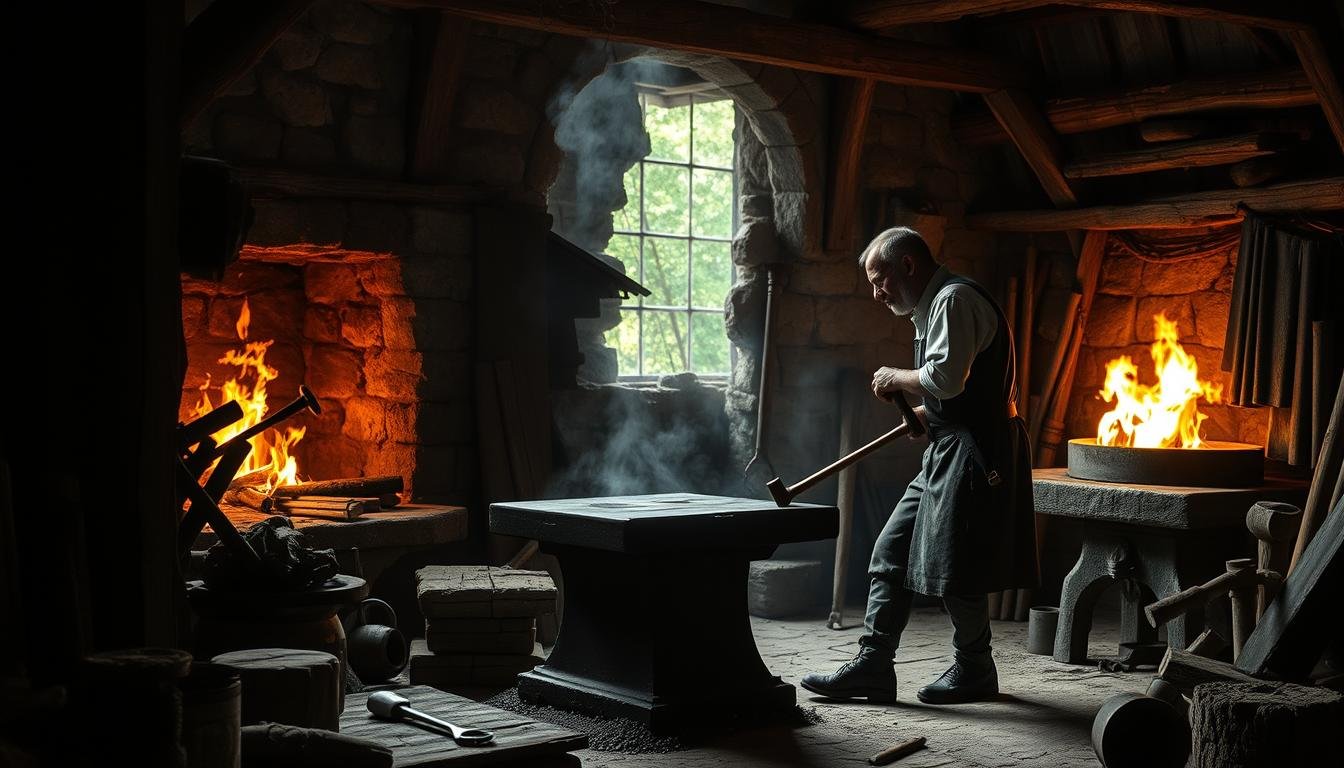
The Evolution of Metal Forging Procedures Through History
Traditional blacksmithing techniques formed the foundation of early metal forging in America
The journey of metal forging in America began with colonial blacksmiths who brought European techniques to the New World. These early craftsmen established small forges where they produced essential tools, horseshoes, and hardware that supported the growing colonies. Their work relied on simple yet effective procedures: heating metal in coal-fired forges, hammering it on anvils, and cooling it to achieve the desired shape and properties.
The Industrial Revolution marked a pivotal turning point for Metal Forging Procedures in the United States. The introduction of steam-powered hammers in the early 19th century dramatically increased production capacity and precision. This innovation allowed forging operations to scale beyond small blacksmith shops into industrial facilities capable of producing larger, more complex components.
The Rise of Industrial Forging in America
By the mid-1800s, the railroad industry became a major driver for forging advancements in America. The demand for rails, locomotive components, and railway hardware pushed forging technology forward. Trip hammers and drop forges became common, enabling the production of standardized parts with greater efficiency. These developments coincided with improved understanding of metallurgy, allowing forgemasters to better control the properties of their products.
The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw further refinement of Metal Forging Procedures with the introduction of hydraulic presses. These machines offered more controlled force application than hammers, resulting in more precise forgings. This period also witnessed the emergence of closed-die forging, which allowed for more complex shapes and tighter tolerances than traditional open-die methods.
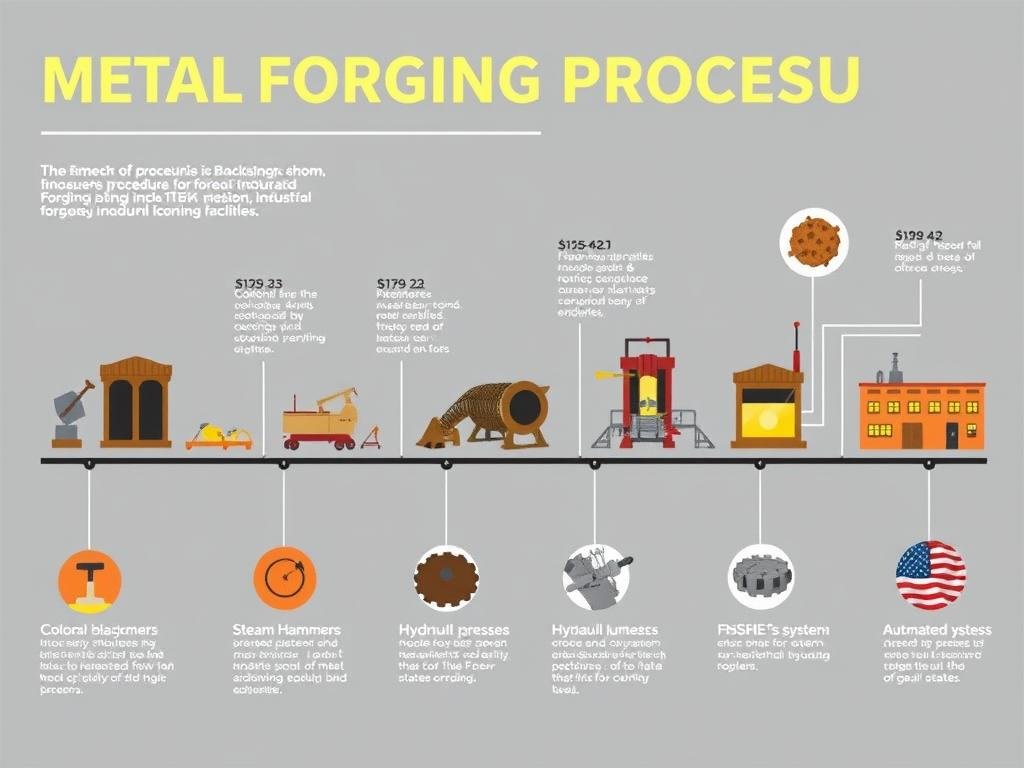
The evolution of forging technology in America from manual techniques to industrial processes
Modern Metal Forging Procedures and Techniques
Today’s metal forging industry bears little resemblance to its historical roots, though the fundamental principles remain unchanged. Modern Metal Forging Procedures employ sophisticated equipment, precise temperature control, and advanced metallurgical knowledge to produce components with exceptional mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy.
Classification of Modern Forging Processes
Contemporary forging processes are typically classified based on temperature and the equipment used:
Temperature-Based Classification
- Cold Forging: Performed at room temperature, offering excellent dimensional accuracy and surface finish but requiring greater force.
- Warm Forging: Conducted at temperatures between room temperature and recrystallization point, balancing formability with precision.
- Hot Forging: Performed above the metal’s recrystallization temperature, allowing for easier deformation and complex shapes.
Equipment-Based Classification
- Open Die Forging: Metal is shaped between flat or simply contoured dies, ideal for large or unique parts.
- Closed Die Forging: Metal is formed in dies containing a cavity that shapes the workpiece, offering greater precision.
- Roll Forging: Metal is passed between rotating rolls to reduce thickness and increase length.
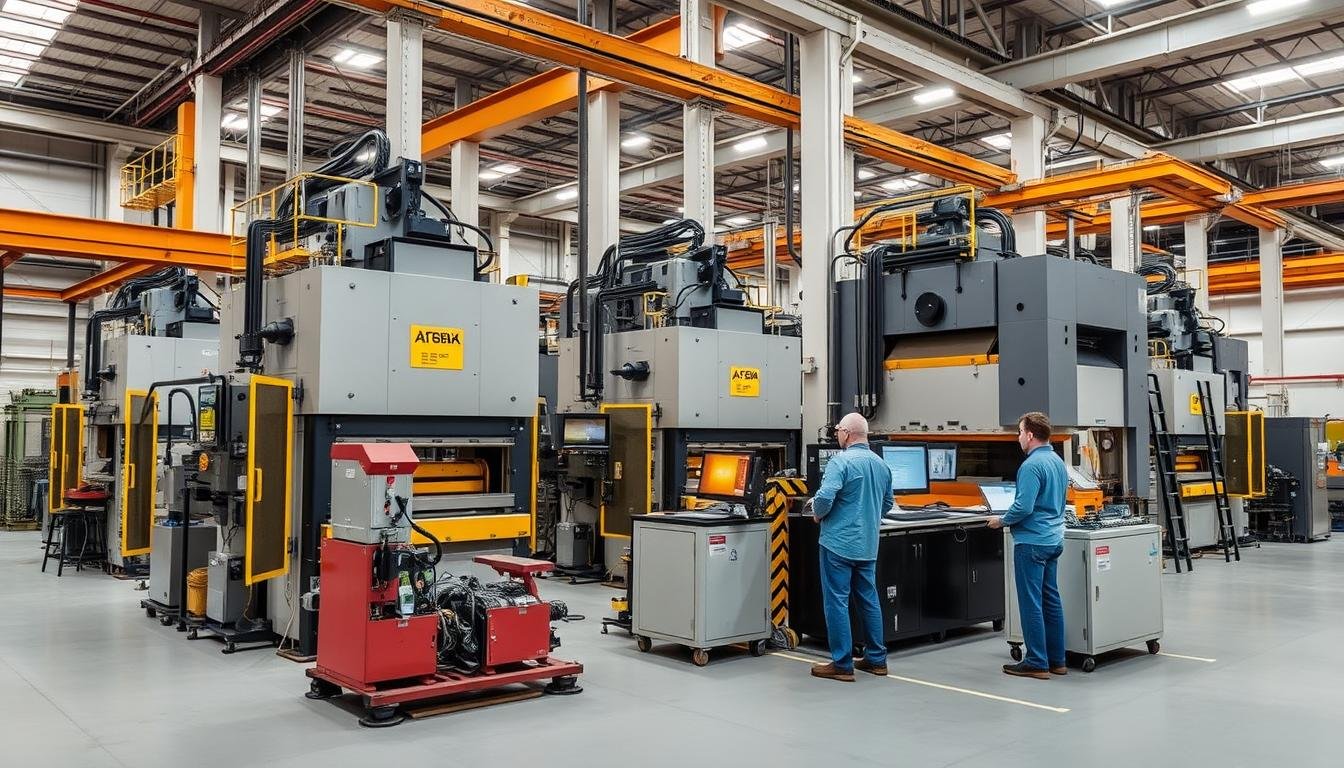

Advanced hydraulic presses and automated systems define modern metal forging operations
The Step-by-Step Metal Forging Procedures
Regardless of the specific technique employed, most modern forging operations follow a similar sequence of procedures:
- Die Design and Manufacturing: Creating precision dies based on the final part requirements, considering material flow, grain structure, and dimensional tolerances.
- Material Selection: Choosing the appropriate metal alloy based on the component’s mechanical requirements and intended application.
- Billet Preparation: Cutting raw material to the required size and weight for the forging process.
- Heating: Raising the metal to the appropriate forging temperature in controlled furnaces. For steel, this typically ranges from 1,550°F to 2,250°F.
- Forging: Applying compressive force to shape the heated metal using hammers, presses, or rollers.
- Trimming: Removing excess material (flash) that forms during the closed-die forging process.
- Heat Treatment: Enhancing mechanical properties through controlled heating and cooling cycles.
- Finishing: Performing secondary operations such as machining, grinding, or surface treatments to achieve final specifications.
- Inspection: Verifying dimensional accuracy and material integrity through various testing methods.
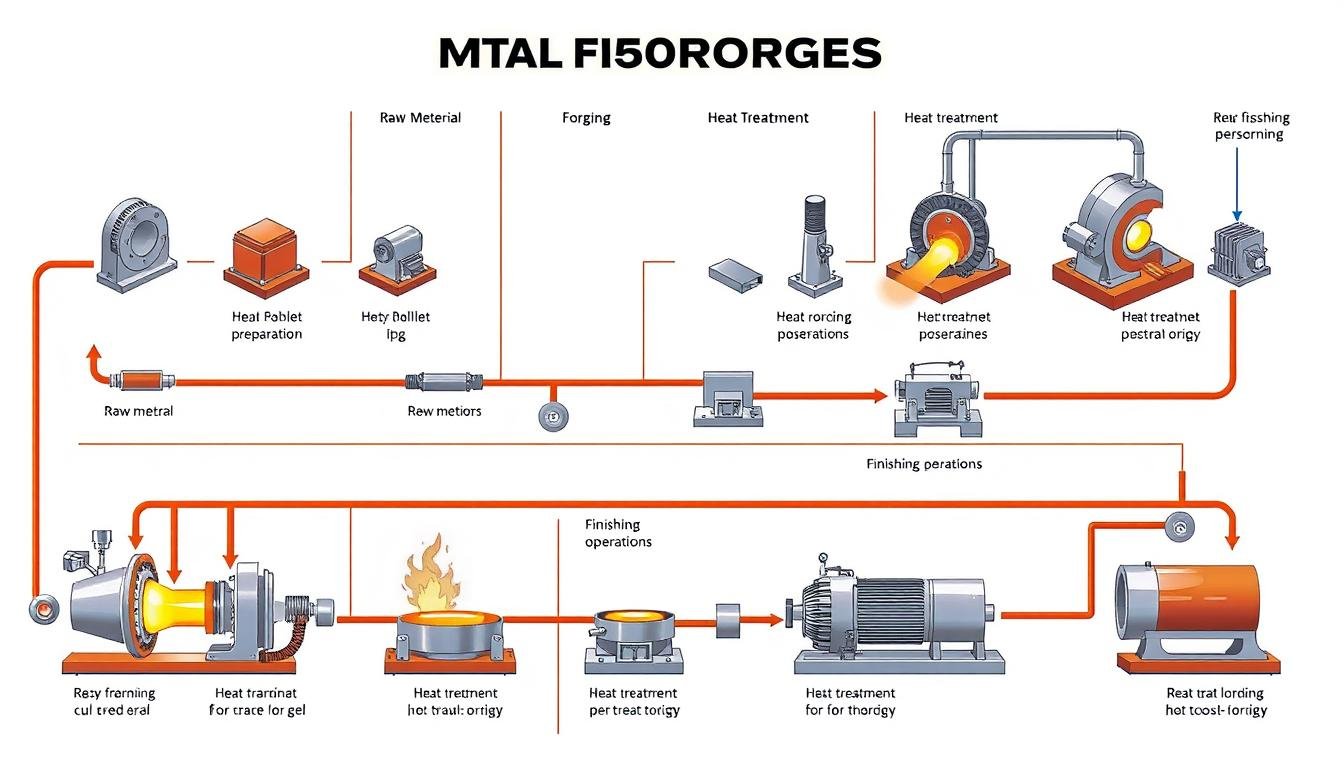
The complete metal forging process from raw material to finished component
Expert Metal Forging Solutions for Your Business
MAIKONG specializes in precision metal forging with 60+ CNC machines and 100+ tons monthly processing capacity. Our team delivers custom components with superior strength and dimensional accuracy.
Get A Quick Quote
Why Metal Forging Procedures Produce Superior Components
The unique advantages of forged components stem directly from the physical processes involved in forging. When metal is compressed under high pressure, its internal grain structure is refined and aligned with the shape of the part. This fundamental change in microstructure results in several key benefits:
Mechanical Advantages
- Enhanced Strength: Forged parts typically exhibit 26% higher tensile strength than cast or machined components.
- Superior Fatigue Resistance: The refined grain structure significantly improves resistance to cyclic loading.
- Improved Impact Toughness: Forged components can absorb energy without fracturing, crucial for safety-critical applications.
- Structural Integrity: The forging process eliminates internal voids and porosity that can compromise performance.
Production Advantages
- Material Efficiency: Near-net-shape forging minimizes material waste compared to machining from solid stock.
- Consistency: Modern forging processes deliver highly repeatable results across production runs.
- Versatility: Forging can be applied to a wide range of metals and alloys, including steel, aluminum, titanium, and copper.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While initial tooling costs may be high, large production runs benefit from economies of scale.
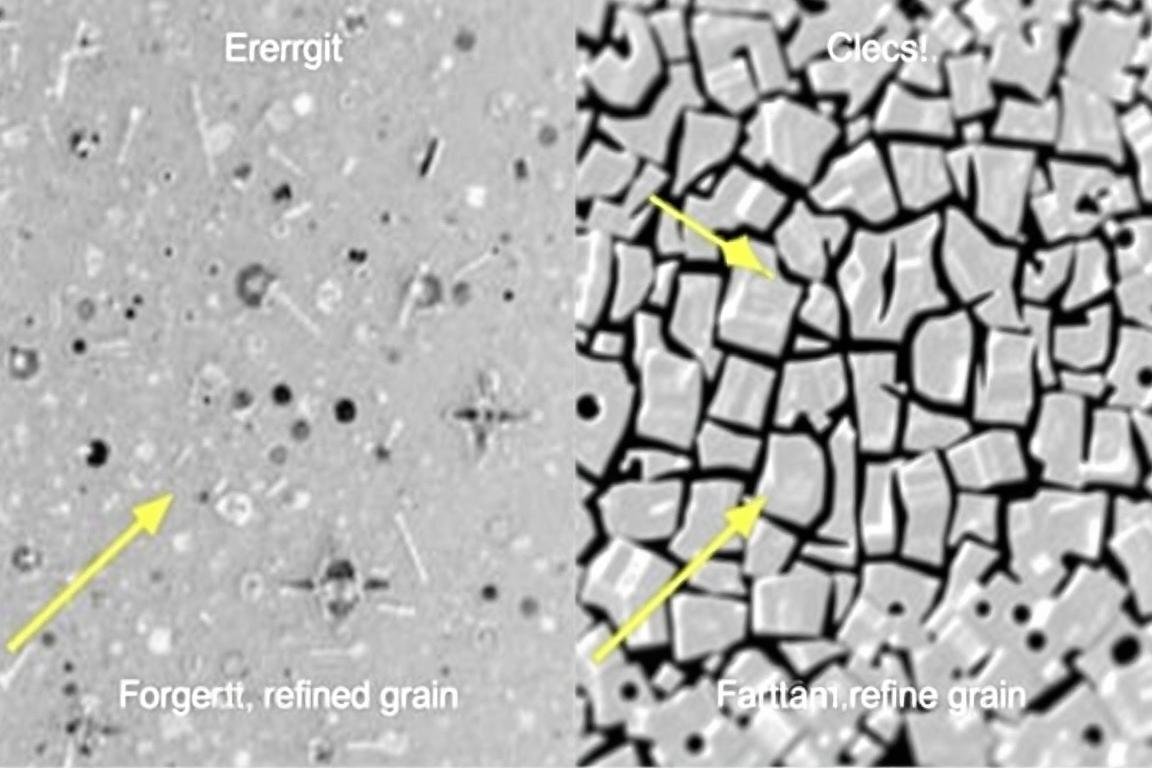

Comparison of grain structure in forged (left) versus cast (right) metal components
Aluminum Forging vs. Casting: A Comprehensive Comparison
When selecting a manufacturing method for aluminum components, understanding the differences between forging and casting is crucial. The following comparison highlights why Metal Forging Procedures often deliver superior results for critical applications:
| Comparison Categories |
Aluminum Forging |
Casting Aluminum |
| Strength and Durability |
Higher due to dense, uniform grain structure |
Potentially lower due to air pockets and inclusions |
| Tensile Properties |
Superior tensile strength and resistance |
Lower tensile strength |
| Fatigue Resistance |
Better resistance against fatigue failure |
Potentially lower fatigue resistance |
| Complex Geometries |
Require multiple steps to achieve complex shapes |
Can achieve complex shapes in one session |
| Dimensional Accuracy |
Better accuracy and tighter tolerances |
Potential inconsistencies |
| Surface Finish |
Smoother surfaces, reduced post-processing |
Might require more machining due to air pockets |
| Weight-to-Strength Ratio |
High strength-to-weight ratio |
Bulkier parts may be needed |
| Ideal Applications |
Aerospace, automotive, medical devices |
Consumer goods, simple parts, non-critical sectors |
Industrial Applications of Metal Forging Procedures
The exceptional mechanical properties of forged components make them ideal for applications where performance, reliability, and safety are paramount. Across the United States, forged parts play critical roles in numerous industries:
Aerospace
The aerospace industry relies on forged components for critical applications where failure is not an option. Jet engine discs, turbine blades, landing gear components, and structural elements benefit from the superior strength-to-weight ratio and fatigue resistance of forged parts.
Automotive
Vehicle performance and safety depend on forged components like crankshafts, connecting rods, transmission gears, and suspension parts. These components must withstand millions of stress cycles while maintaining dimensional stability under extreme conditions.
Oil & Gas
The harsh environments encountered in oil and gas extraction demand components that can withstand high pressures, corrosive conditions, and extreme temperatures. Forged valves, fittings, wellhead components, and tool joints provide the necessary durability.
Heavy Equipment
Construction and agricultural machinery subject components to punishing loads and abrasive conditions. Forged gears, axles, linkages, and structural elements deliver the necessary strength and wear resistance for these demanding applications.
Defense
Military applications require components that perform reliably under extreme conditions. Forged parts are used in weapons systems, vehicles, aircraft, and naval vessels where performance and durability are mission-critical.
Medical
Surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and medical device components benefit from the biocompatibility, strength, and precise dimensional control offered by specialized forging procedures.

Forged components serve critical functions across diverse industries
Need Custom Forged Components?
Contact MAIKONG today to discuss your specific requirements. Our team of experts will help you select the optimal materials and forging procedures for your application.
Or email us at: Lucy@maikongforge.us
MAIKONG’s Advanced Metal Forging Procedures and Capabilities
At MAIKONG, we combine traditional forging expertise with cutting-edge technology to deliver superior metal components. Our comprehensive manufacturing capabilities ensure that we can meet the most demanding specifications while maintaining competitive pricing and reliable delivery schedules.
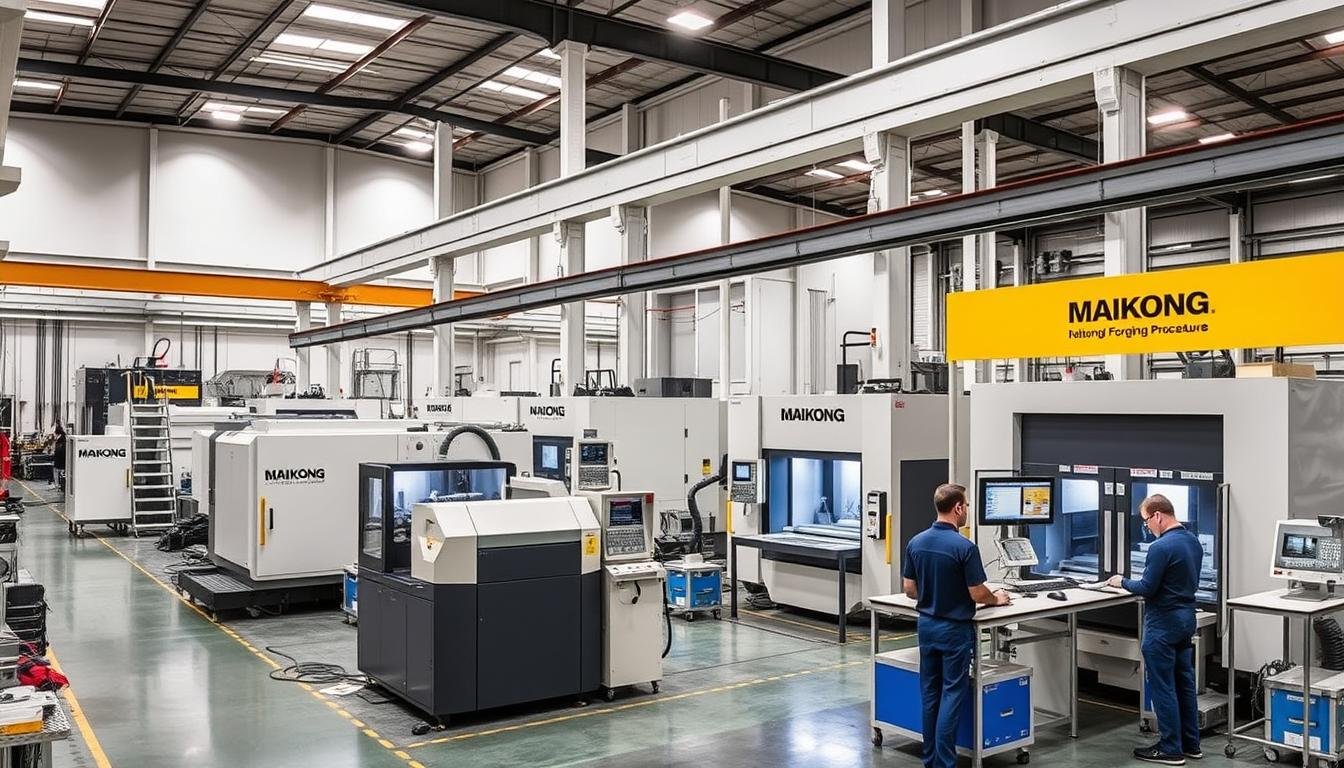

MAIKONG’s state-of-the-art manufacturing facility in GD, SZ
Our Manufacturing Capabilities
CNC Turning Services
MAIKONG’s CNC turning capabilities deliver precision cylindrical components with superior surface finishes. Our advanced turning centers produce deep holes, machined threads, and complex profiles with exceptional accuracy and consistency.
CNC Milling Services
Our multi-axis CNC milling equipment creates complex prismatic shapes and flat surfaces with precise dimensional control. These flexible systems require no fixed tooling, allowing for rapid production of both prototypes and production runs.
Swiss Type Machining
MAIKONG specializes in precision small parts and long shaft components through our Swiss-type machining services. Our dual-spindle, multi-axis equipment provides one-stop solutions with exceptional accuracy.
Our Comprehensive Forging Process
MAIKONG’s full-service approach ensures quality and consistency at every stage of the forging process:
Pre-Production Services
- CAD/CAM Engineering: Advanced analysis software identifies and mitigates potential issues early in the design phase.
- Material Selection: Comprehensive evaluation of mechanical properties, machinability, heat treatment characteristics, and cost-effectiveness.
- Tooling Design: Precision die design ensures initial quality, while regular maintenance preserves consistency.
Production Capabilities
- Forging Workshop: Equipped to accommodate diverse aluminum forging specifications.
- Heat Treatment: In-house facilities with comprehensive statistical analysis and documentation.
- Precision Machining: State-of-the-art CNC machines capable of intricate forging machining operations.
- Surface Treatment: Enhancing appearance, performance, and competitiveness of finished products.
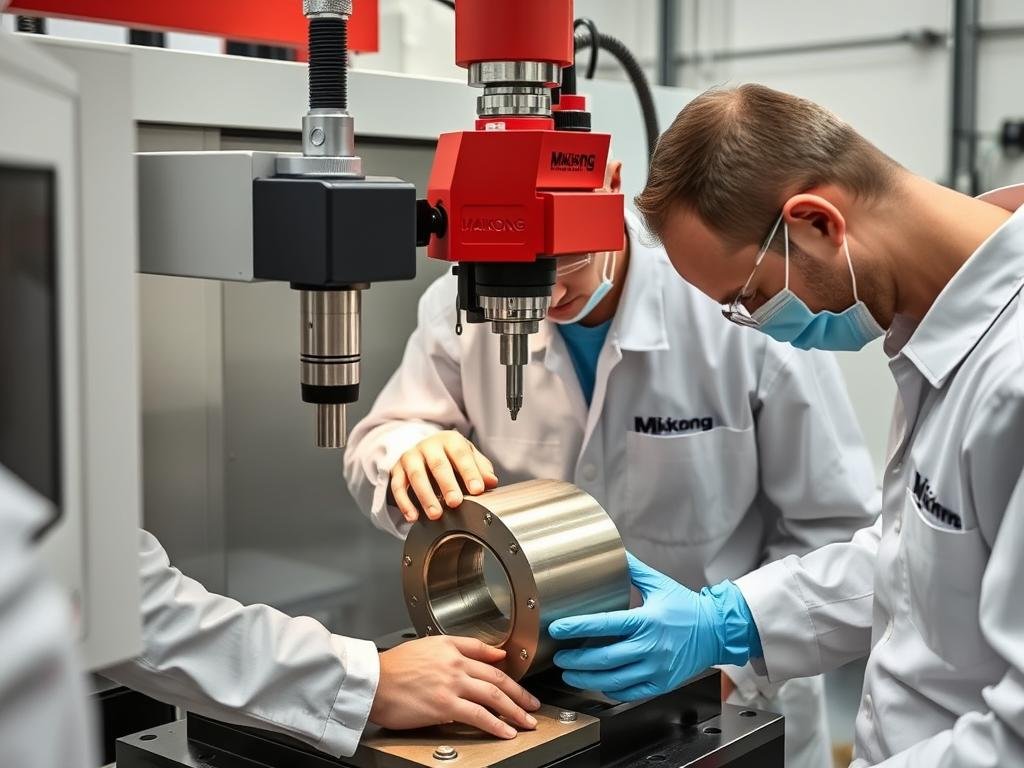

Rigorous quality control ensures MAIKONG’s forged components meet the highest standards
Materials Optimized for Metal Forging Procedures
The selection of appropriate materials is crucial to successful forging operations. At MAIKONG, we work with a wide range of metals and alloys, each offering specific advantages for different applications:
Carbon & Alloy Steels
These versatile materials offer excellent strength, hardness, and wear resistance at competitive costs. Common grades include 1045, 4140, and 4340, each providing different combinations of properties to suit specific applications.
Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum forgings deliver an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for aerospace and automotive applications. Popular forging alloys include 6061, 7075, and 2024, each offering different combinations of strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability.
Stainless Steels
Combining strength with excellent corrosion resistance, stainless steel forgings are perfect for demanding environments. Grades like 304, 316, and 17-4 PH serve applications ranging from food processing equipment to marine components.
Titanium Alloys
With the highest strength-to-weight ratio of any metal and exceptional corrosion resistance, titanium forgings excel in aerospace, medical, and chemical processing applications. Ti-6Al-4V is the most widely used titanium forging alloy.
Copper Alloys
Brass and bronze forgings offer excellent electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and non-sparking properties. These materials are ideal for electrical components, marine hardware, and applications in potentially explosive environments.
Nickel-Based Superalloys
For extreme temperature applications, superalloys like Inconel, Hastelloy, and Monel provide exceptional strength and oxidation resistance at temperatures exceeding 2000°F, making them essential for jet engines and gas turbines.

MAIKONG works with diverse metal alloys to meet specific application requirements
Become a MAIKONG Distributor in the US
MAIKONG is actively seeking distribution partners across the United States. Join us in delivering high-quality, cost-effective metal forging solutions to American manufacturers.
Partner With Us
Quality Assurance in Metal Forging Procedures
At MAIKONG, quality is built into every step of our manufacturing process. Our comprehensive quality management system ensures that each component meets or exceeds customer specifications and industry standards.
Our Quality Control Approach
Material Verification
Before production begins, we verify the chemical composition and mechanical properties of all raw materials. Our in-house testing laboratory ensures that only materials meeting our strict specifications enter the production process.
In-Process Inspection
Throughout the forging process, our technicians perform regular dimensional checks and visual inspections to catch any deviations before they become problems. Statistical process control methods help us maintain consistent quality across production runs.
Non-Destructive Testing
We employ various NDT methods including ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle inspection, and dye penetrant testing to detect any internal or surface defects that might compromise component integrity.
Final Inspection
Every finished component undergoes thorough inspection for dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and mechanical properties. Our ISO 9001:2015 certified quality management system ensures complete documentation and traceability.
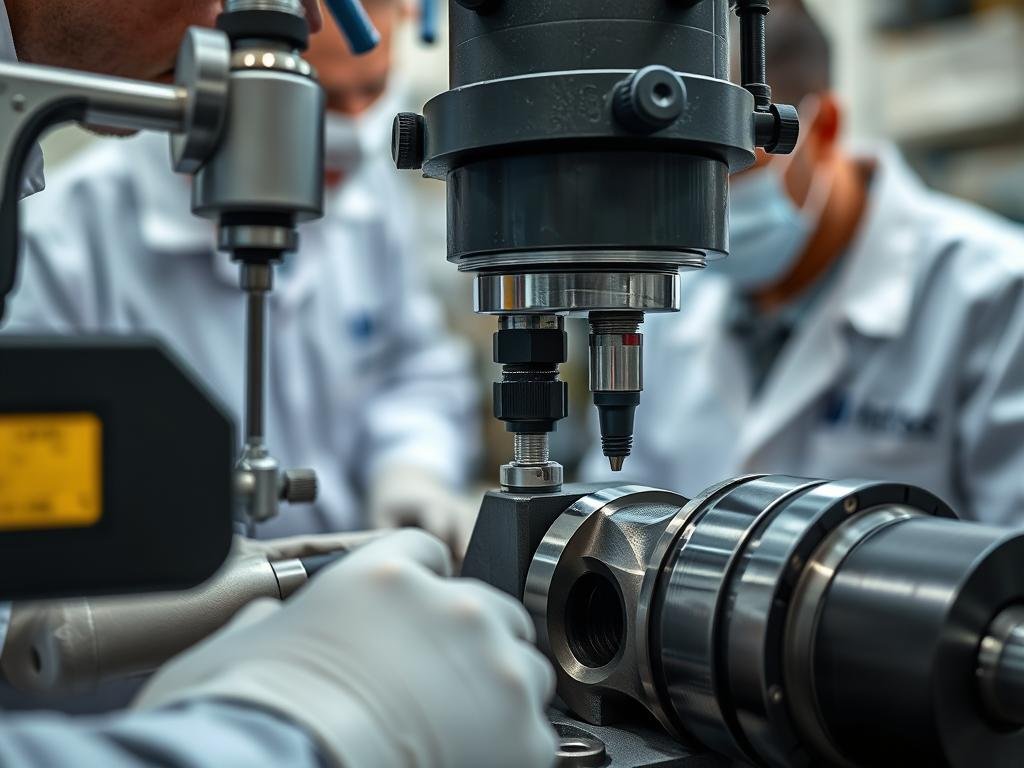

Comprehensive testing ensures MAIKONG’s forged components meet the highest quality standards
MAIKONG Forging Gallery
Below are examples of precision components manufactured using our advanced Metal Forging Procedures:
The Future of Metal Forging Procedures
As we look to the future, metal forging continues to evolve with advancements in materials science, simulation technology, and automation. These innovations are making forging processes more efficient, precise, and environmentally sustainable.
At MAIKONG, we remain at the forefront of these developments, continuously investing in new technologies and processes to deliver superior forged components. Our commitment to quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction positions us as a trusted partner for manufacturers across industries.
Whether you need precision aluminum forgings, steel components, or custom brass parts, MAIKONG has the expertise, equipment, and experience to meet your requirements. Our comprehensive capabilities—from design and material selection through forging, machining, and finishing—ensure that we can deliver complete solutions that perform in the most demanding applications.
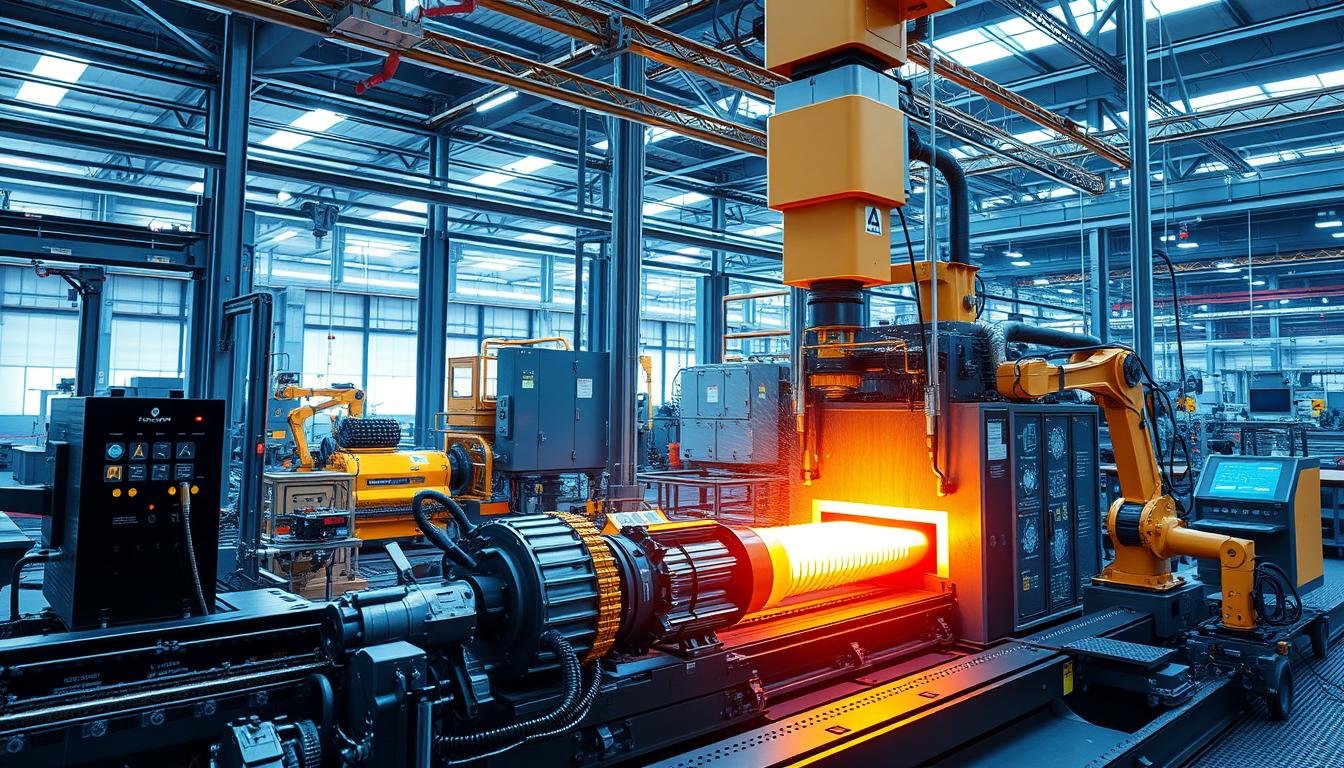

The future of metal forging combines traditional expertise with cutting-edge technology
Ready to Discuss Your Metal Forging Needs?
Contact MAIKONG today to learn how our advanced forging capabilities can deliver superior components for your application.














