The Complete Guide to Forging Procedures for US Industrial Manufacturers & Engineers
Forging Procedures represent one of the oldest and most reliable metal shaping techniques in manufacturing. This comprehensive guide explores the essential processes, techniques, and applications of modern forging operations. Whether you’re an engineer, manufacturer, or procurement specialist, understanding these procedures is crucial for producing high-strength, durable components that meet rigorous industrial standards.

Understanding Forging Procedures and Their Importance
Forging is a manufacturing process that shapes metal through compressive forces, creating parts with superior strength characteristics compared to cast or machined components. The internal grain structure of forged metal follows the shape of the part, resulting in exceptional structural integrity and reliability at high stress points.
Modern forging operations combine traditional metalworking principles with advanced technology
For critical “cannot fail” components in aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery applications, forging procedures deliver unmatched performance. At MAIKONG, we’ve refined these techniques to provide US manufacturers with exceptional quality forged components at competitive prices.
Need Expert Forging Services?
MAIKONG offers comprehensive metal forging solutions with superior strength-to-weight ratios and competitive pricing.
Get A Quick Quote
Classification of Forging Processes
Forging processes can be classified based on temperature, equipment used, and the specific techniques employed. Each approach offers distinct advantages depending on the material, desired properties, and application requirements.
Classification by Temperature
Hot Forging
Conducted at temperatures above the metal’s recrystallization point (typically 0.6 times its melting point). This process allows for significant deformation with relatively low force requirements but may result in less precise dimensions and rougher surface finish.
Warm Forging
Performed at intermediate temperatures between hot and cold forging. This approach balances formability with precision, offering a good compromise for many applications.
Cold Forging
Executed at room temperature or slightly elevated temperatures below recrystallization. Cold forging delivers excellent dimensional accuracy and surface finish but requires greater force and is limited in the degree of deformation possible.
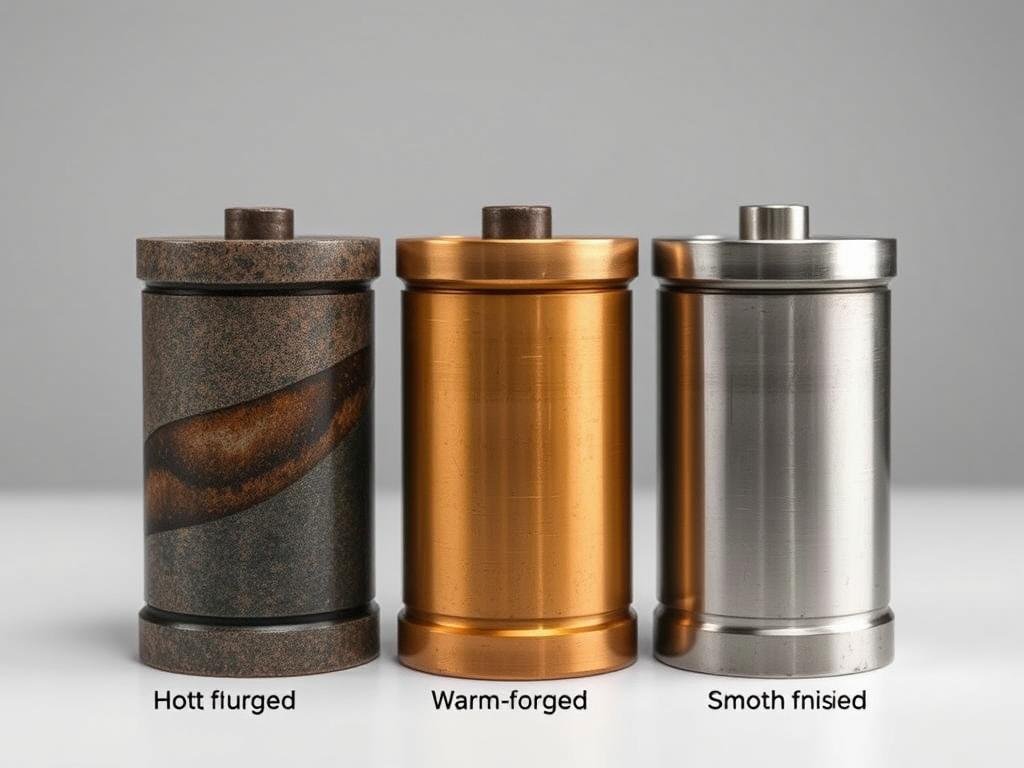

Comparison of surface finish quality between hot, warm, and cold forging techniques
Types of Forging Methods
Modern manufacturing employs various forging methods, each suited to specific applications and production requirements. At MAIKONG, we utilize multiple techniques to deliver optimal results for our clients.
Open Die Forging
In open die forging, metal is shaped between multiple strikes of a hammer on a flat or simply shaped die. This versatile method is ideal for large or custom components with simple geometries.
Closed Die Forging
Also known as impression die forging, this process shapes metal within the cavity of two dies that contain the negative of the desired part shape. Ideal for complex geometries and high-volume production.
Rolled Ring Forging
Specialized process for creating seamless rings by punching a hole in a round metal stock and then rolling and shaping it to the desired dimensions. Commonly used for bearings, gears, and aerospace components.
Explore Our Forging Capabilities
MAIKONG specializes in precision forging for critical components. Contact our engineering team to discuss your specific requirements.
Contact via WhatsApp
Essential Steps in the Forging Procedures
The forging process involves several critical stages that must be carefully controlled to ensure optimal results. Each step contributes to the final product’s quality, dimensional accuracy, and mechanical properties.
The complete forging workflow from raw material selection to finished component
Step 1: Die Design and Manufacturing
The foundation of successful forging begins with precise die design. Using advanced CAD/CAM systems, engineers create dies that will shape the metal into the desired form. Die quality directly impacts the final product’s dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and production efficiency.
Step 2: Material Selection and Preparation
Selecting the appropriate metal alloy and preparing it for forging is crucial. The material must have the right composition and properties to achieve the desired characteristics in the finished product. At MAIKONG, we carefully source and test all raw materials to ensure consistency and quality.
Step 3: Heating
Most forging operations require heating the metal to increase its plasticity. The specific temperature depends on the material and forging method. For steel, temperatures typically range from 850°C to 1150°C for hot forging, while aluminum forging temperatures are generally around 400-500°C.
Step 4: Forging Operation
During the actual forging operation, the heated metal is shaped using pressure applied by presses or hammers. This may involve multiple stages to gradually form the metal into the desired shape. The specific equipment and techniques used depend on the complexity of the part and production volume requirements.
Industrial forging press applying controlled pressure to shape metal components
Step 5: Trimming and Finishing
After forging, excess material (flash) is removed through trimming operations. Additional finishing processes may include machining, heat treatment, and surface treatments to achieve the final dimensions and properties required.
Step 6: Quality Control and Inspection
Rigorous quality control ensures that forged components meet all specifications. This may include dimensional inspection, material testing, and non-destructive evaluation techniques to verify structural integrity.
Advantages of Forging Over Other Manufacturing Methods
| Comparison Categories |
Aluminum Forging |
Casting Aluminum |
| Strength and Durability |
Higher due to dense, uniform grain structure |
Potentially lower due to air pockets and inclusions |
| Tensile Properties |
Superior tensile strength and resistance |
Lower tensile strength |
| Fatigue Resistance |
Better resistance against fatigue failure |
Potentially lower fatigue resistance |
| Dimensional Accuracy |
Better accuracy and tighter tolerances |
Potential inconsistencies |
| Weight-to-Strength Ratio |
High strength-to-weight ratio |
Bulkier parts may be needed |
The forging process creates components with exceptional mechanical properties that cannot be achieved through casting or machining alone. By aligning the grain structure of the metal, forging enhances strength, durability, and resistance to fatigue and impact.
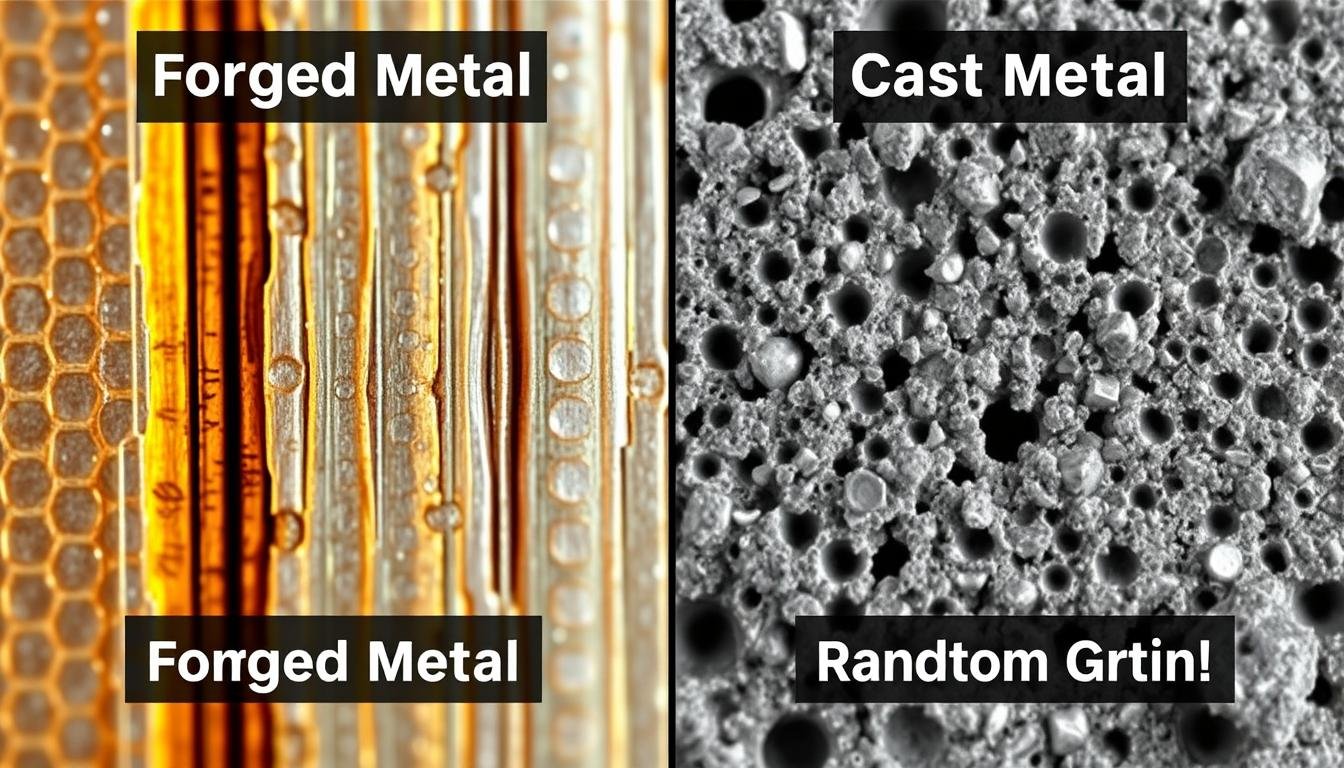
Microscopic comparison showing aligned grain structure in forged metal (left) versus random grain structure in cast metal (right)
MAIKONG’s Comprehensive Forging Capabilities
At MAIKONG, we offer a complete range of forging and machining services to meet the diverse needs of US industrial manufacturers. Our state-of-the-art facilities and experienced team ensure exceptional quality and value.
Our Forging Services
- Aluminum Forging Services
- Steel Forging
- Brass Forging
- Open and Closed Die Forging
- Precision Forging
- Custom Metal Parts
CNC Machining Capabilities
- CNC Milling Services
- CNC Turning Services
- Precision CNC Machining
- Custom CNC Parts
- CNC Prototyping
- Contract Manufacturing CNC
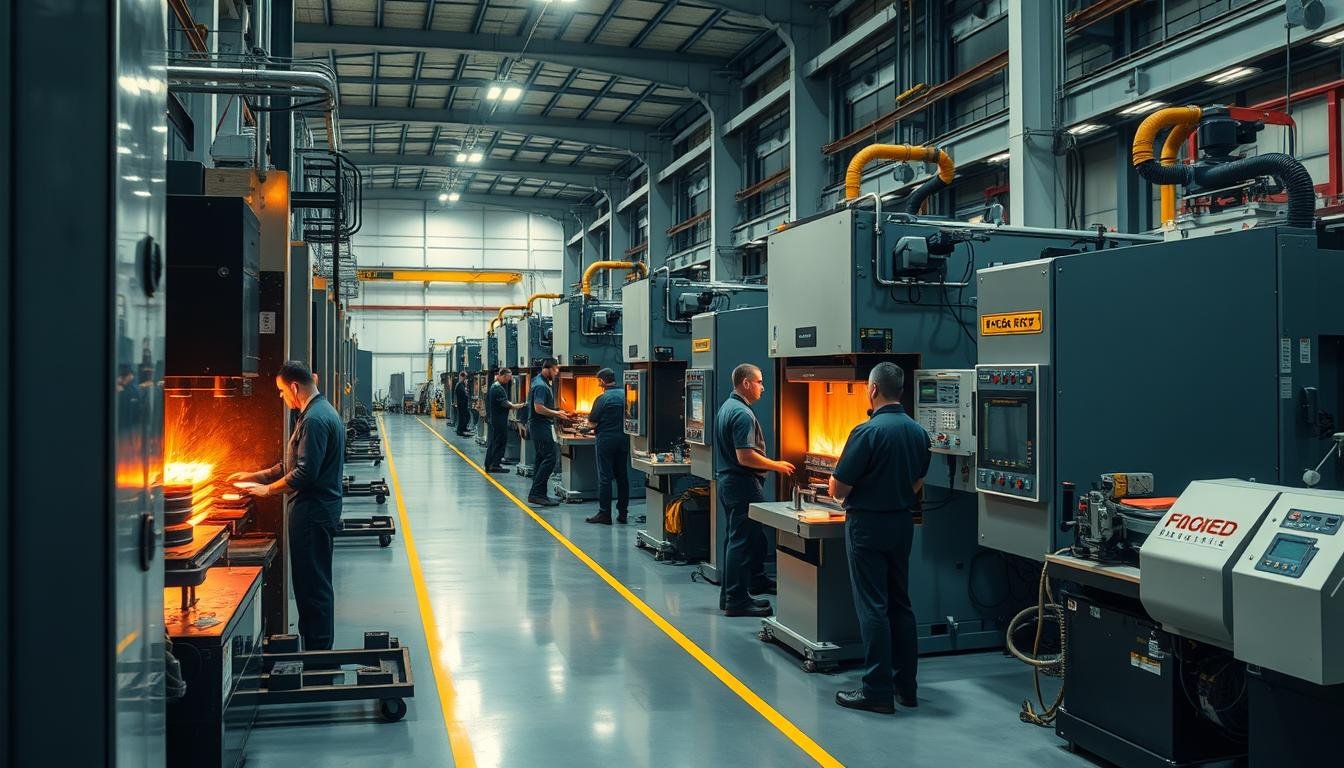

MAIKONG’s state-of-the-art forging facility in GD, SZ
Partner with MAIKONG for Your Forging Needs
We’re currently seeking distribution partners and agents across the United States. Experience our exceptional quality and competitive pricing firsthand.
Become a Distribution Partner
Quality Assurance in Forging Procedures
Quality control is integral to every stage of our forging process. MAIKONG implements rigorous testing and inspection protocols to ensure that all components meet or exceed industry standards and customer specifications.
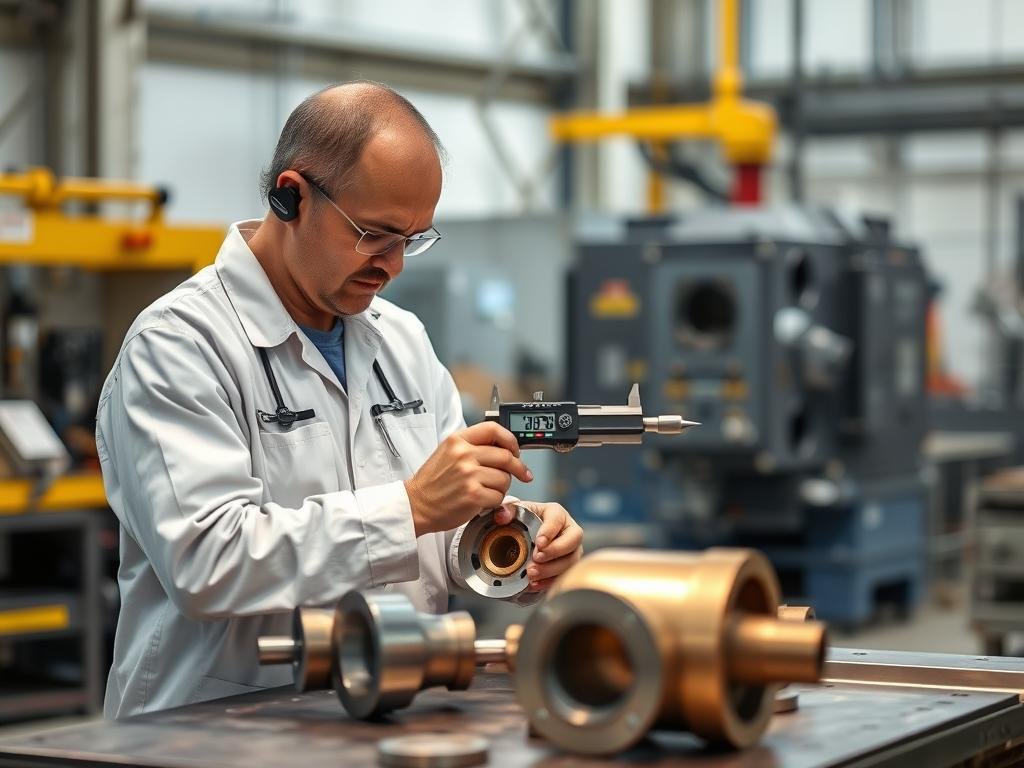

Precision inspection ensures dimensional accuracy of every forged component
Our Quality Control Measures Include:
- Material certification and testing
- In-process inspection during forging
- Dimensional verification using precision equipment
- Non-destructive testing (ultrasonic, magnetic particle, dye penetrant)
- Mechanical property testing (tensile, hardness, impact)
- Surface finish inspection
- Final quality verification before shipping
Our commitment to quality ensures that every component we produce meets the highest standards of performance and reliability. This dedication has made MAIKONG a trusted partner for US manufacturers across various industries.
Industries Served by MAIKONG’s Forging Solutions
Our forging expertise serves a wide range of industries that require high-performance metal components. We understand the unique requirements of each sector and tailor our forging procedures accordingly.
Automotive
Crankshafts, connecting rods, transmission components, and steering parts that require exceptional strength and durability.
Aerospace
Structural components, landing gear parts, and engine components that must meet rigorous safety and performance standards.
Industrial Machinery
Gears, shafts, and structural elements for heavy equipment that operate under extreme conditions.
Other industries we serve include oil and gas, power generation, mining, construction, and agriculture. Our versatile capabilities allow us to meet the diverse needs of US manufacturers across the industrial spectrum.
Conclusion: Advancing Manufacturing Through Superior Forging
Forging procedures continue to evolve with advances in materials science, equipment technology, and process control. As a leader in metal forging and machining, MAIKONG remains at the forefront of these developments, providing US manufacturers with components that meet the highest standards of quality and performance.
By combining traditional forging expertise with modern technology and rigorous quality control, we deliver solutions that help our clients succeed in today’s competitive global marketplace. Contact MAIKONG today to learn how our forging capabilities can enhance your manufacturing operations.