Selecting the Right Materials for Metal Forging
Material selection is a critical first step in the Metal Forging Procedure. Different metals and alloys respond uniquely to forging processes, affecting both the manufacturing approach and the final component properties.
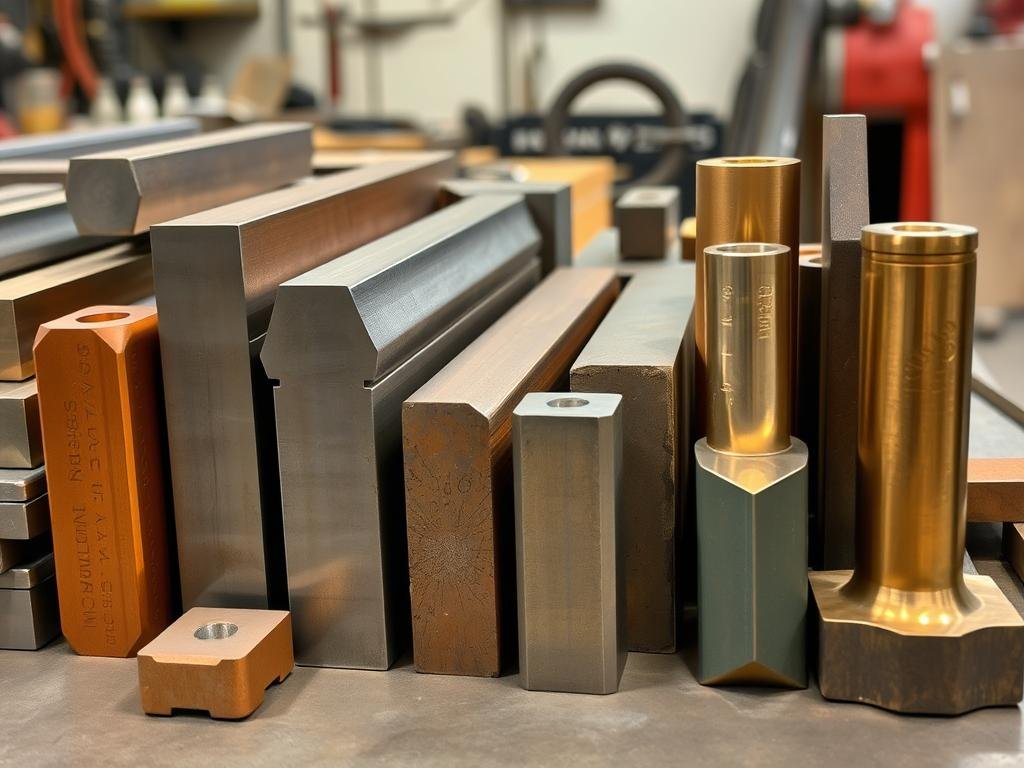

Various metal billets prepared for forging, including aluminum, steel, and brass alloys
Commonly Forged Metals and Their Applications
| Metal Type |
Forging Temperature |
Key Properties |
Common Applications |
| Carbon Steel |
1100-1250°C |
High strength, good ductility, excellent value |
Gears, crankshafts, connecting rods |
| Alloy Steel |
1050-1200°C |
Enhanced strength, heat resistance, wear resistance |
Heavy machinery, power generation, oil & gas |
| Stainless Steel |
1100-1250°C |
Corrosion resistance, high temperature stability |
Valves, fittings, medical instruments |
| Aluminum |
350-500°C |
Lightweight, corrosion resistant, good conductivity |
Aerospace components, automotive parts |
| Titanium |
870-980°C |
Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, biocompatible |
Aerospace, medical implants, chemical processing |
| Brass |
700-800°C |
Good corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity |
Valves, plumbing fixtures, decorative hardware |
The Advantage of Aluminum Forging over Casting
At MAIKONG, we specialize in aluminum forging, which offers significant advantages over cast aluminum for many applications. The following comparison highlights why forged aluminum is often the superior choice for critical components:
Aluminum Forging Advantages
- Higher strength due to dense, uniform grain structure
- Superior tensile strength and resistance
- Better resistance against fatigue failure
- Better dimensional accuracy and tighter tolerances
- Smoother surfaces with reduced post-processing
- More responsive to heat treatment for controlled properties
- Directional grain flow for improved mechanical properties
- Higher strength-to-weight ratio
Casting Aluminum Limitations
- Potentially lower strength due to air pockets and inclusions
- Lower tensile strength overall
- Reduced fatigue resistance
- Potential dimensional inconsistencies
- May require more machining due to surface defects
- Less predictable response to heat treatment
- No directional grain structure
- Bulkier parts may be needed for equivalent strength
Expert Material Selection for Your Application
Not sure which metal is right for your forging project? MAIKONG’s engineering team can help you select the optimal material based on your application requirements, performance needs, and budget constraints.
Get Expert Material Advice
The Core Stages of the Metal Forging Procedure
The Metal Forging Procedure involves several critical stages, each contributing to the quality and performance of the final component. At MAIKONG, we’ve refined this process to ensure optimal results for every project.
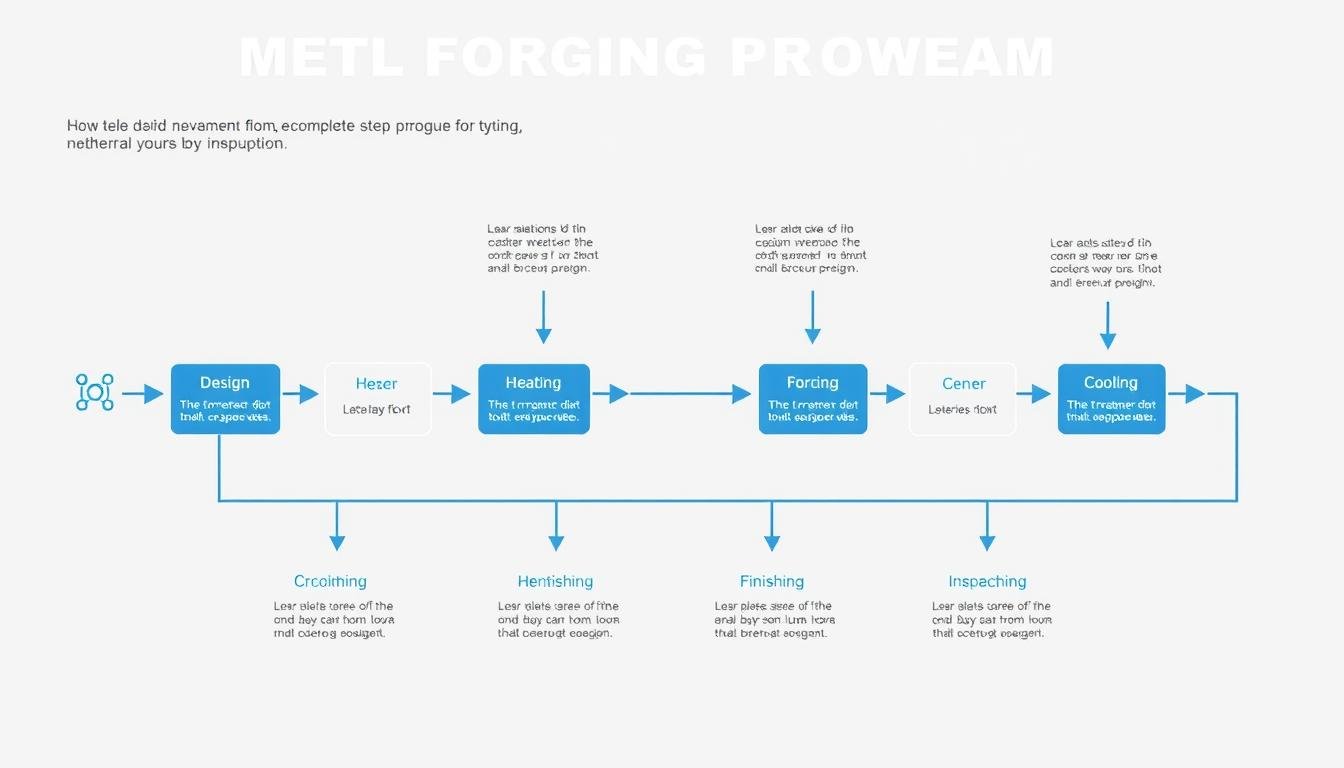
Complete metal forging procedure flowchart from initial design to final inspection
1. Design and Engineering
Every successful forging project begins with thorough design and engineering. This critical first stage of the Metal Forging Procedure establishes the foundation for all subsequent steps.
CAD/CAM Development
Our engineering team utilizes advanced computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software to create precise digital models of your components. This technology allows us to:
- Visualize the final component before production begins
- Optimize designs for the forging process
- Identify and resolve potential issues early
- Reduce development time and costs
Simulation and Analysis
Before any metal is heated, we conduct comprehensive simulations to predict how materials will behave during forging. Our analysis includes:
- Finite element analysis (FEA) to predict material flow
- Stress and strain calculations
- Die fill simulation to ensure complete forming
- Thermal modeling to optimize heating parameters
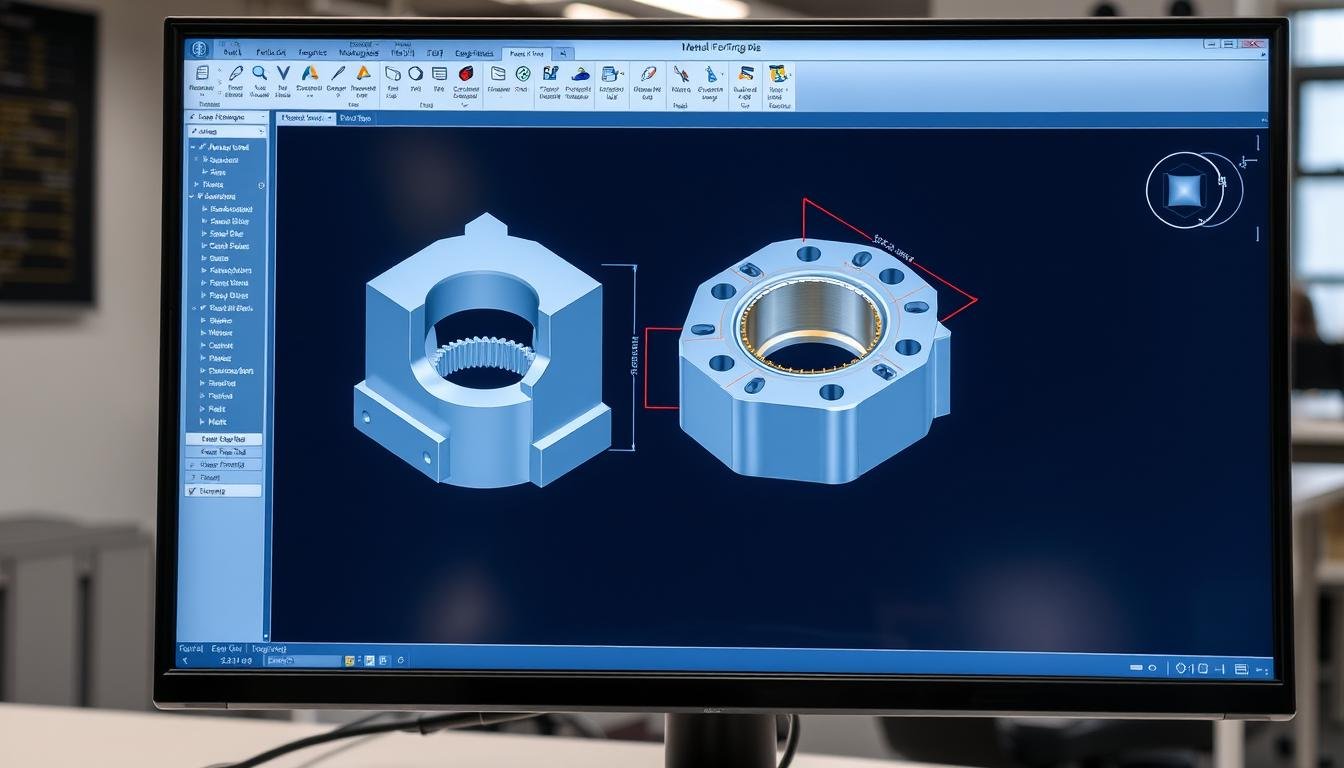
MAIKONG engineers use advanced CAD/CAM software to design optimal forging dies
2. Die Design and Manufacturing
Die design is a critical element in the Metal Forging Procedure that directly impacts the quality, efficiency, and cost of production. At MAIKONG, we invest significant resources in creating precision dies that deliver superior results.
- Material Selection – We use premium tool steels with appropriate hardness, wear resistance, and thermal properties for each application
- Precision Machining – Our CNC machining centers create dies with exacting tolerances
- Heat Treatment – Specialized heat treatment ensures optimal die hardness and durability
- Surface Finishing – Polishing and surface treatments reduce friction and extend die life
- Regular Maintenance – Systematic inspection and maintenance preserve die quality throughout production
3. Material Preparation
Proper material preparation ensures consistent results in the Metal Forging Procedure. This stage involves several important steps:
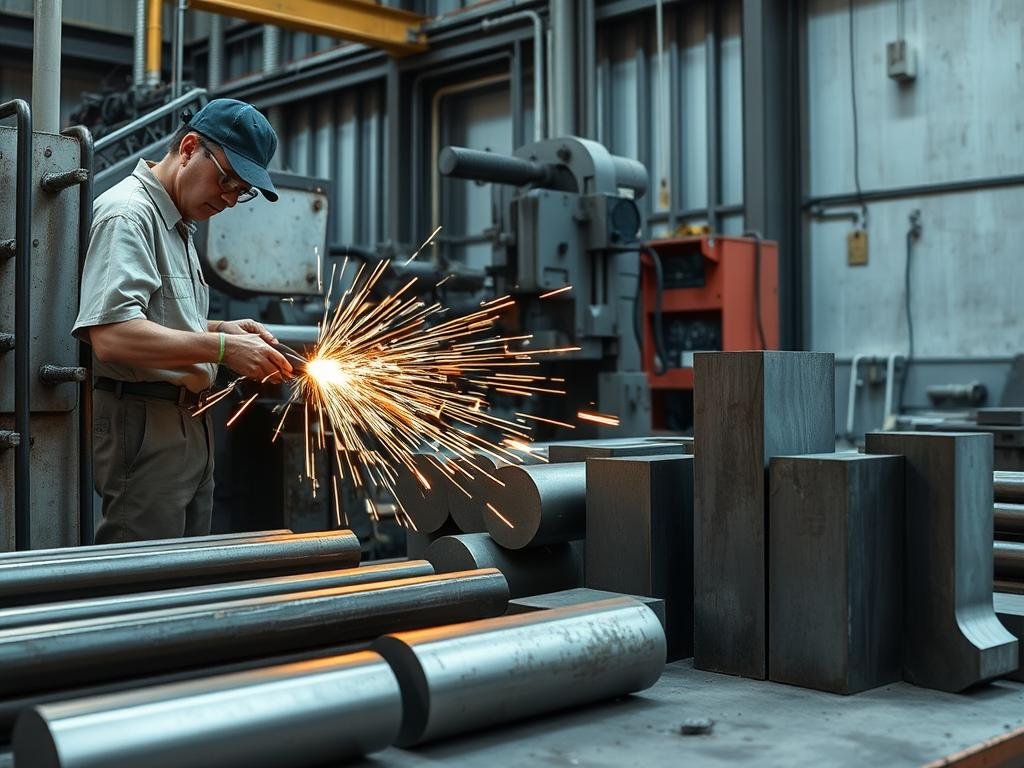

Precise cutting of metal billets ensures optimal material usage and forging quality
- Material Testing – Chemical composition and mechanical properties are verified
- Cutting to Size – Raw material is cut to precise dimensions based on the final part requirements
- Surface Preparation – Cleaning and preparation remove contaminants that could affect forging quality
- Preforming – For complex shapes, initial forming may be performed to prepare for the main forging operation
4. Heating
Heating is a fundamental step in the Metal Forging Procedure that directly impacts material formability and final part properties. The specific temperature depends on the metal being forged and the desired characteristics of the finished component.
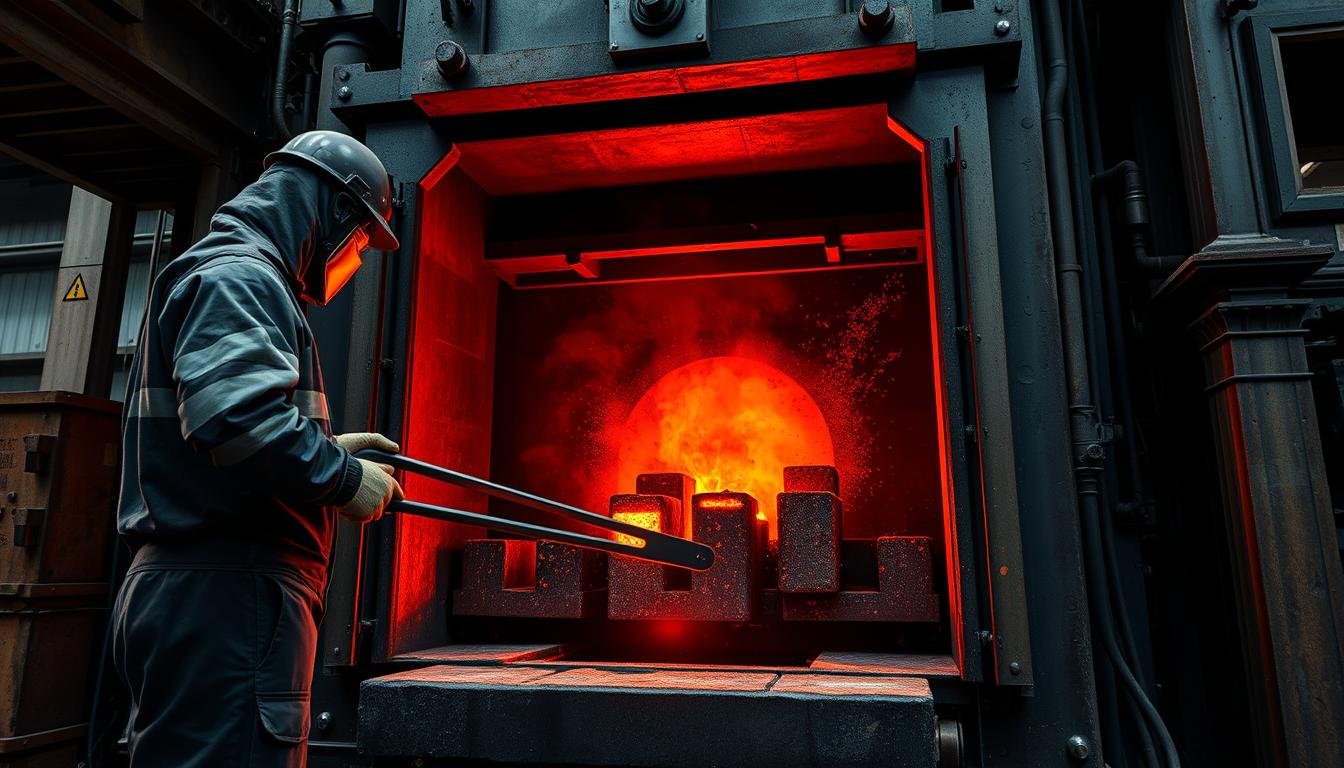

Precise temperature control during heating ensures optimal metal plasticity for forging
Temperature Control
MAIKONG utilizes advanced temperature monitoring systems to ensure precise heating:
- Computer-controlled furnaces maintain exact temperatures
- Multiple temperature zones ensure uniform heating
- Thermal imaging verifies proper temperature distribution
- Automated systems prevent overheating or underheating
Heating Methods
We employ various heating technologies based on material and production requirements:
- Gas-fired furnaces for large-scale production
- Electric induction heating for precise control
- Resistance heating for specialized applications
- Zoned heating for complex geometries
5. Forging Operation
The core forging operation is where the heated metal is shaped using controlled pressure. MAIKONG employs various forging methods depending on the component requirements.
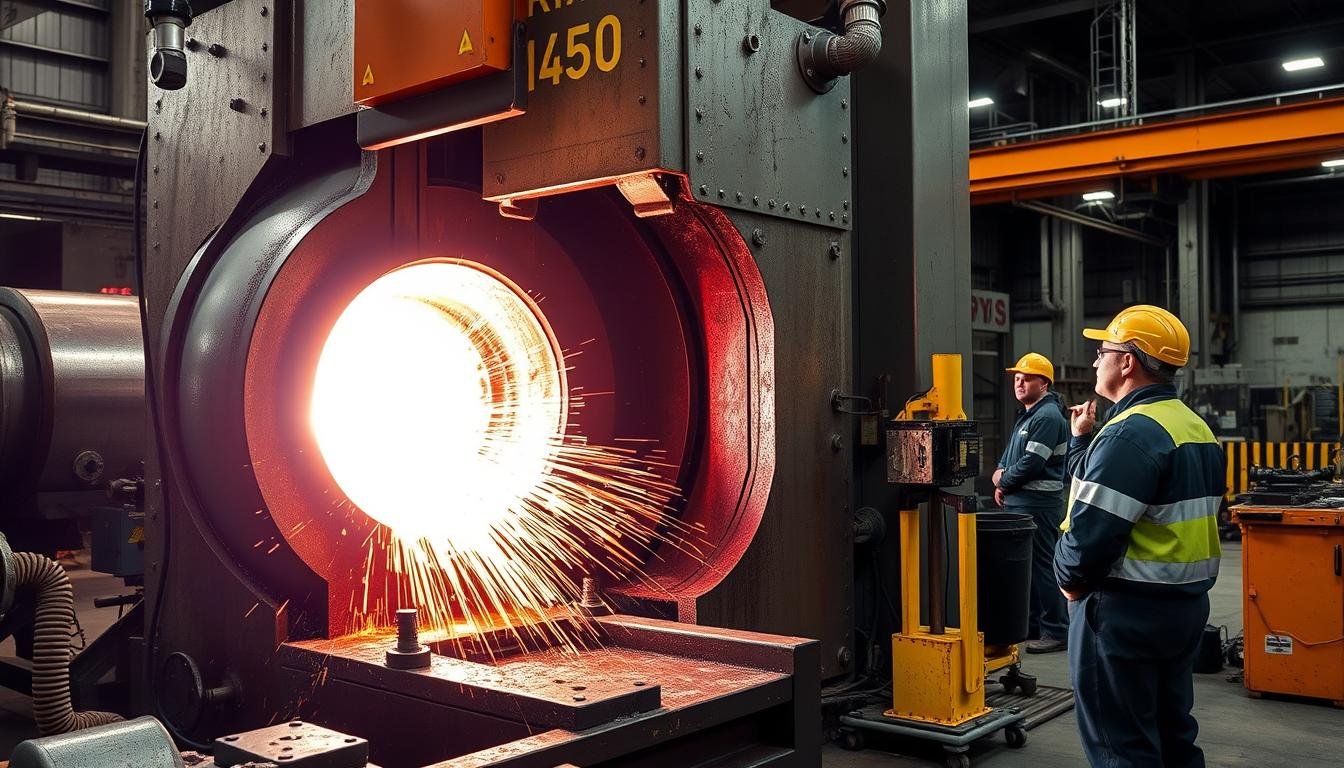

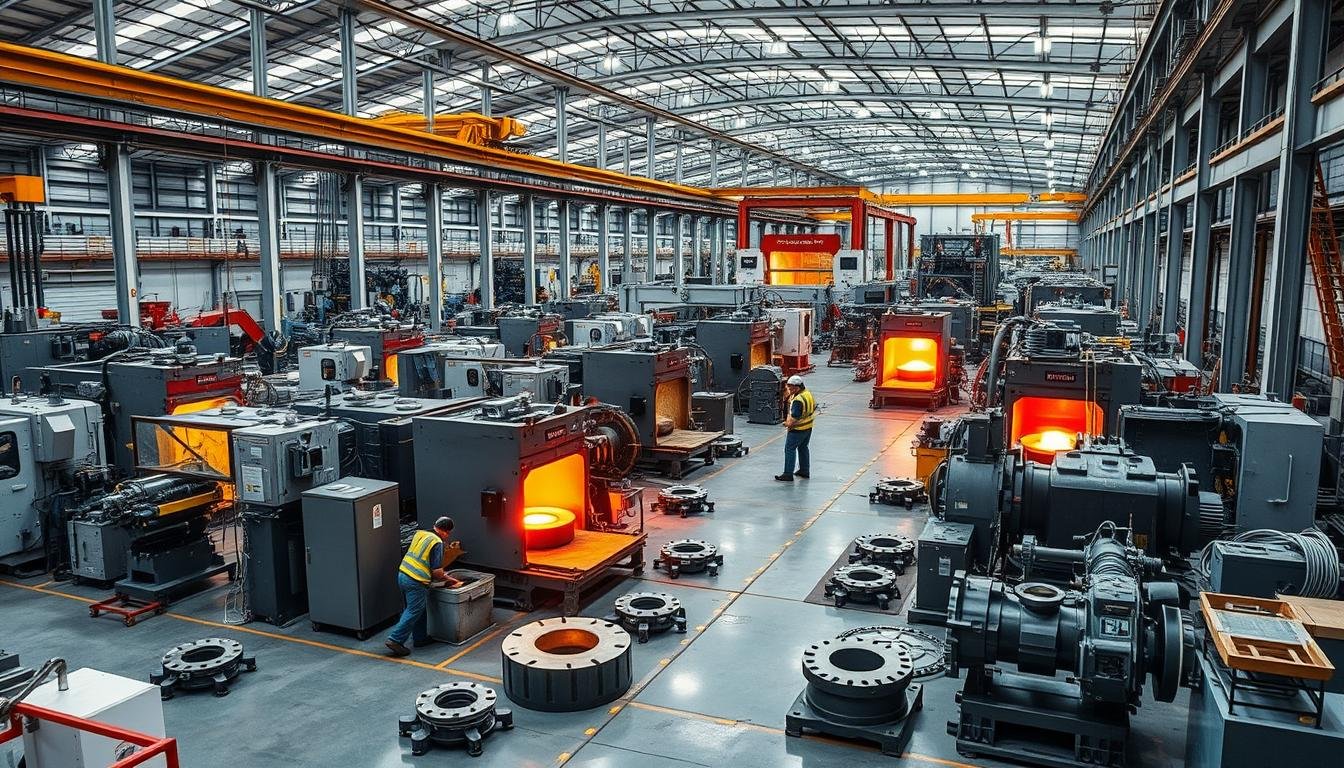
Closed die forging operation at MAIKONG’s advanced manufacturing facility
Open Die Forging
In open die forging, the metal is shaped between flat or simply shaped dies. This method is ideal for:
- Large components with simple geometries
- Low to medium production volumes
- Applications requiring excellent grain flow
- Parts that will undergo significant machining after forging
Closed Die Forging
Closed die forging uses cavity dies to control material flow into a specific shape. This method offers:
- Complex geometries with tight tolerances
- Efficient material utilization
- Reduced machining requirements
- Excellent repeatability for high-volume production
Roll Forging
Roll forging passes metal between rotating rolls to gradually form the desired cross-section. Benefits include:
- Efficient production of elongated parts
- Excellent grain flow in the longitudinal direction
- Good dimensional control
- Reduced material waste
6. Cooling and Heat Treatment
After the forging operation, controlled cooling and heat treatment are essential to achieve the desired mechanical properties. This stage of the Metal Forging Procedure significantly influences the final performance characteristics of the component.
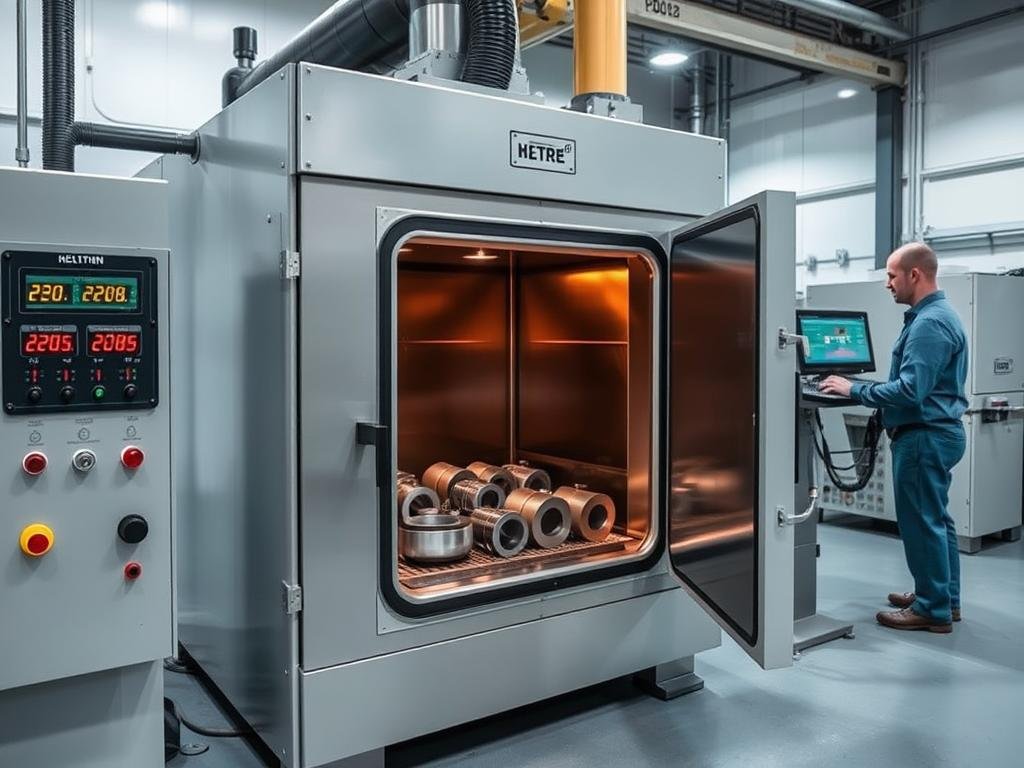

Precision heat treatment enhances the mechanical properties of forged components
- Controlled Cooling – Carefully managed cooling rates prevent internal stresses and distortion
- Annealing – Relieves internal stresses and improves machinability
- Normalizing – Refines grain structure and enhances mechanical properties
- Quenching – Rapid cooling in oil, water, or polymer solutions increases hardness
- Tempering – Reduces brittleness while maintaining appropriate hardness levels
- Solution Treatment – For aluminum alloys, dissolves alloying elements into solid solution
- Aging – Precipitation hardening improves strength in certain alloys
7. Finishing Operations
The final stages of the Metal Forging Procedure involve various finishing operations to achieve the required dimensions, surface quality, and appearance.
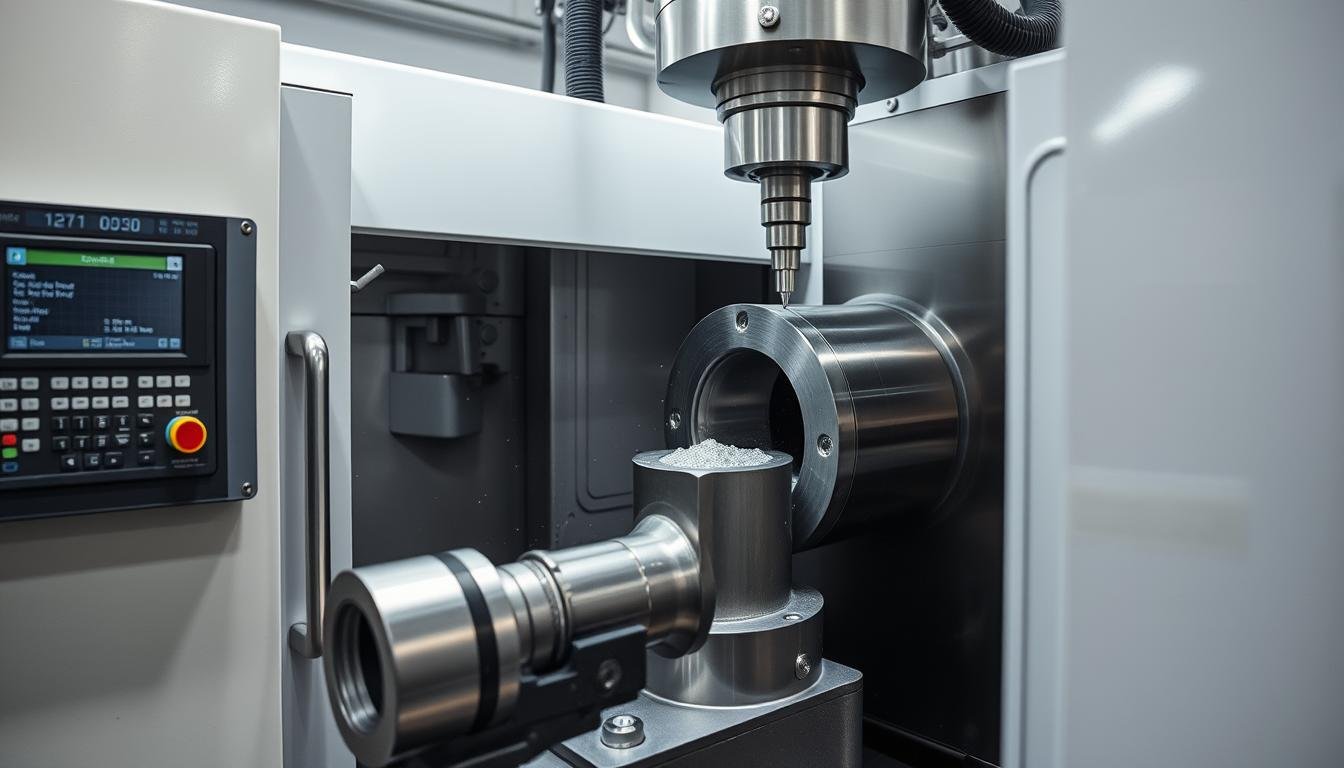

Precision CNC machining brings forged components to final dimensions and tolerances
Mechanical Finishing
- Trimming – Removes excess flash from closed die forgings
- Machining – CNC operations achieve final dimensions and features
- Grinding – Creates precise surfaces and improves finish quality
- Shot Blasting – Cleans surfaces and improves appearance
Surface Treatments
- Anodizing – Creates protective oxide layer on aluminum
- Painting – Provides corrosion protection and aesthetic appeal
- Plating – Enhances surface properties and appearance
- Passivation – Improves corrosion resistance of stainless steel
8. Quality Control and Inspection
Rigorous quality control is integrated throughout the Metal Forging Procedure at MAIKONG. Our comprehensive inspection processes ensure that every component meets or exceeds specifications.
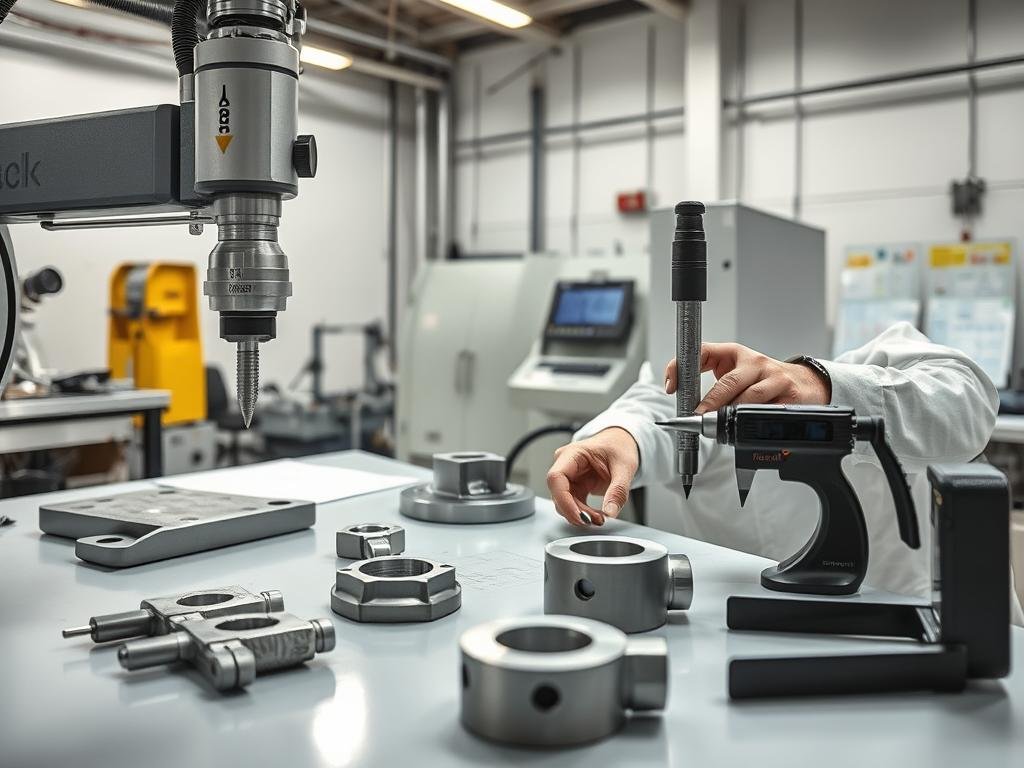

Comprehensive quality inspection ensures every forged component meets exact specifications
- Dimensional Inspection – Coordinate measuring machines (CMM) verify critical dimensions
- Visual Inspection – Trained inspectors identify surface defects and inconsistencies
- Non-Destructive Testing – Ultrasonic, magnetic particle, and dye penetrant testing detect internal flaws
- Mechanical Testing – Hardness testing, tensile testing, and impact testing verify mechanical properties
- Chemical Analysis – Spectrographic analysis confirms material composition
- Documentation – Comprehensive quality records maintain traceability
Experience MAIKONG’s Superior Forging Quality
Our rigorous quality control and advanced forging procedures ensure components that meet the most demanding specifications. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements.
Request a Quote
Conclusion: Mastering the Metal Forging Procedure
The Metal Forging Procedure represents a perfect blend of ancient craftsmanship and modern engineering. From initial design through final inspection, each stage contributes to creating components with exceptional strength, durability, and performance. At MAIKONG, we’ve mastered this process to deliver superior forged components for the most demanding applications.
Whether you need aluminum, steel, or brass forgings, our comprehensive capabilities and commitment to quality ensure optimal results for your specific requirements. Our one-stop manufacturing solution includes design assistance, material selection, forging, machining, heat treatment, and surface finishing—all under one roof for maximum efficiency and quality control.
Ready to experience the MAIKONG difference? Contact our team today to discuss your metal forging needs and discover how our expertise can enhance your products and operations.
Get Started with MAIKONG Today
Take the first step toward superior forged components by contacting our expert team. We’re ready to discuss your project requirements and provide a competitive quote.
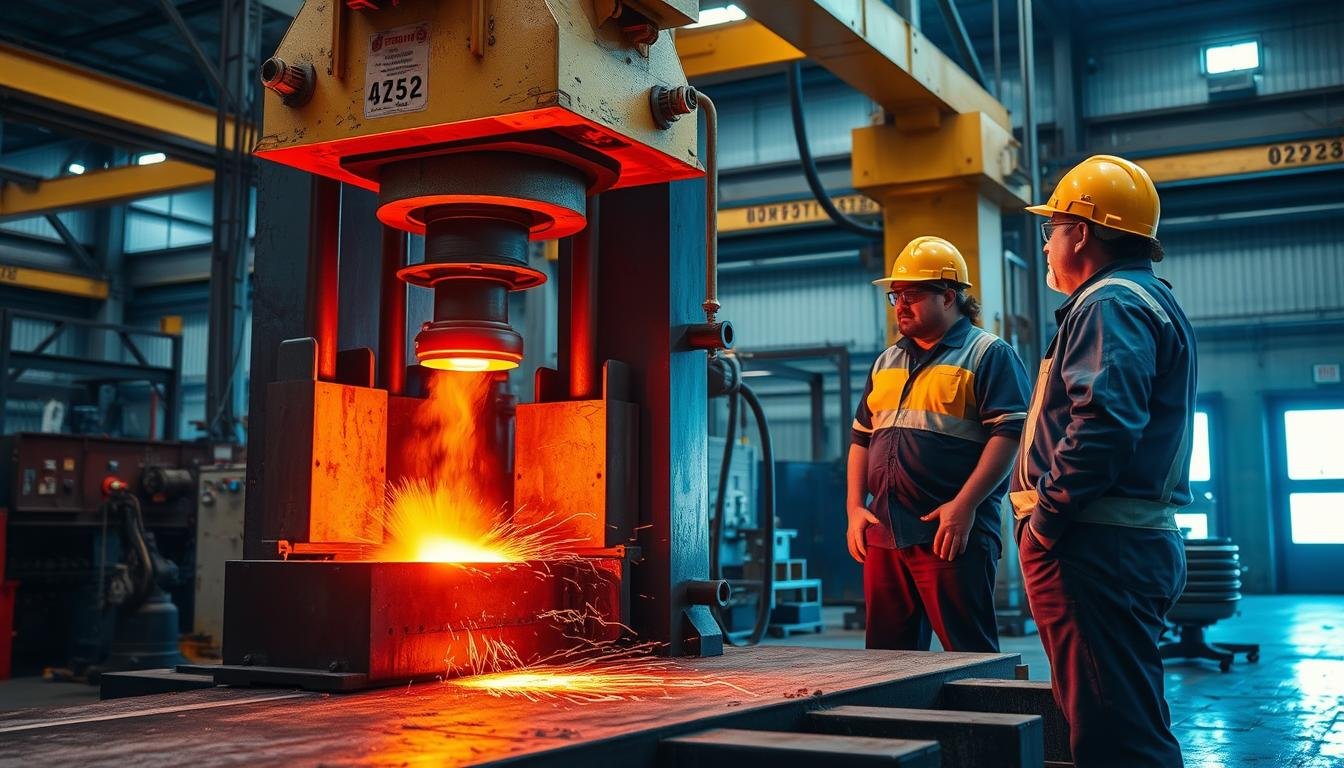
 The metal forging process transforms raw material into high-strength components through controlled deformation
The metal forging process transforms raw material into high-strength components through controlled deformation









